Institutions are the backbone of a functioning democracy—they ensure laws are implemented, justice is served, and governance runs smoothly. In Class 9 Social Science Civics Chapter 4 – Working of Institutions, students learn how India’s key democratic institutions—the legislature, executive, and judiciary—function, interact, and maintain a balance of power. This chapter explains the roles of different institutions in decision-making and highlights how their coordination is essential for democracy to work effectively.
1. Short Notes from Ch 4 : Working of Institutions
- Institutions Definition: Structures like legislature, executive, judiciary that manage governance. Ensure rules and procedures are followed.
- Role in Democracy: Rulers work within these institutions. Balances power and resolves disputes.
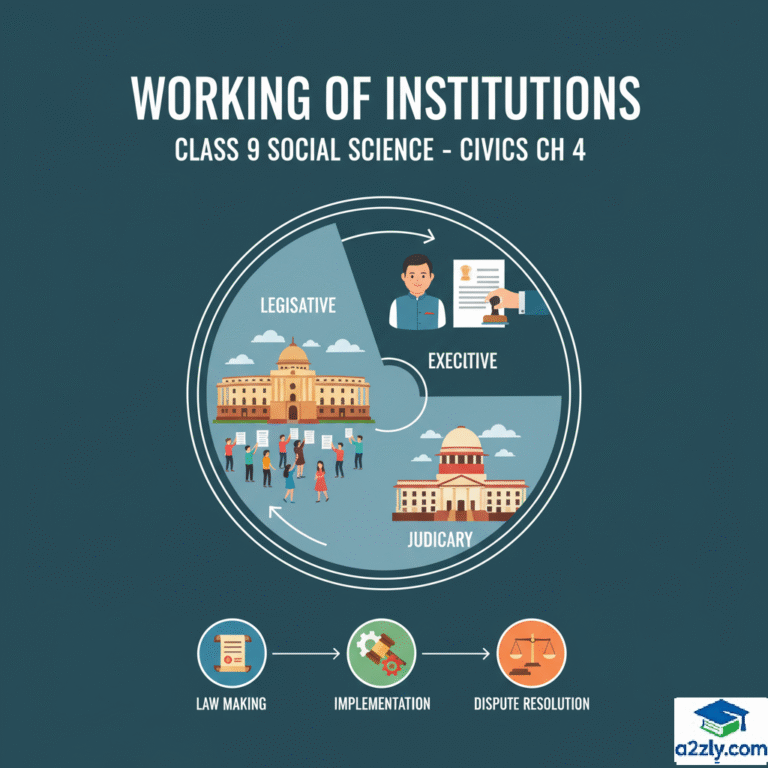
- Legislature: Makes laws, represents people. In India, Parliament (Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha) is key.
- Executive: Implements laws, runs daily administration. Includes Prime Minister, Council of Ministers.
- Judiciary: Interprets laws, resolves disputes. Supreme Court and High Courts ensure justice.
- Interconnection: Legislature passes laws, executive executes, judiciary checks legality. Works as a system.
- Democratic Functioning: Transparency, accountability, public participation. Avoids autocracy.
- Central Government: Union Government of India handles national issues. Examples: defense, foreign policy.
- State Examples: State legislatures, chief ministers handle local governance. Varies by region.
- Comparison: Differs from US (stronger states) or UK (monarchy influence). Reflects India’s federal setup.
2. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- Institutions mean: A) Buildings B) Governance structures C) Parties D) Individuals
- Role in democracy: A) Unlimited power B) Balance power C) Ignore rules D) No role
- Legislature’s job: A) Execute laws B) Make laws C) Judge cases D) Administer
- Executive includes: A) Judges B) Prime Minister C) MPs D) Lawyers
- Judiciary’s role: A) Law-making B) Dispute resolution C) Policy execution D) Voting
- Interconnection example: A) No link B) Law to execution C) Separate work D) Random
- Democratic feature: A) Secrecy B) Transparency C) Dictatorship D) No checks
- Central Government handles: A) Local roads B) Defense C) Schools D) Markets
- State example: A) Parliament B) Chief Minister C) President D) Supreme Court
- Compared to US: A) Same B) Stronger states C) No difference D) Weak center
Answer Key: 1-B, 2-B, 3-B, 4-B, 5-B, 6-B, 7-B, 8-B, 9-B, 10-B
3. Very Short Answer Type Questions (VSAQs)
- What are institutions? Answer: Governance structures like legislature, executive, judiciary.
- Role in democracy? Answer: Balance power, follow rules.
- Legislature’s task? Answer: Makes laws.
- Who is in executive? Answer: Prime Minister, ministers.
- Judiciary’s job? Answer: Resolves disputes.
- Interconnection? Answer: Law to execution to justice.
- Democratic trait? Answer: Transparency.
- Central Government focus? Answer: Defense, foreign policy.
- State leader? Answer: Chief Minister.
- US difference? Answer: Stronger states.
4. Short Answer Type Questions (SAQs)
- Define institutions. Answer: Institutions are structures like legislature, executive, judiciary. They manage governance and enforce rules.
- Why needed in democracy? Answer: Ensure rulers follow procedures, balance power. Prevent autocratic rule.
- What does legislature do? Answer: Makes laws, represents people. India’s Parliament is an example.
- Role of executive? Answer: Implements laws, runs administration. Led by the Prime Minister.
- Judiciary’s function? Answer: Interprets laws, resolves disputes. Supreme Court leads this.
- How are they connected? Answer: Legislature makes laws, executive implements, judiciary checks. Forms a balanced system.
- What makes it democratic? Answer: Transparency, accountability, public involvement. Avoids misuse of power.
- Central Government tasks? Answer: Handles defense, foreign policy. Oversees national issues.
- State government example? Answer: Chief Minister leads, manages local governance. Varies by state.
- Comparison with US? Answer: US has stronger states, unlike India’s central focus. Reflects federal differences.
5. Long Answer Type Questions (LAQs)
- What are institutions and their role in democracy? Answer: Institutions are structured bodies like the legislature, executive, and judiciary that manage governance in a democracy. They ensure rulers follow rules, balance power, and resolve disputes, preventing any single entity from dominating. For example, India’s Parliament makes laws, the executive runs the country, and the judiciary upholds justice, together sustaining democratic values.
- Explain the functions of the legislature. Answer: The legislature, such as India’s Parliament, is responsible for making laws that govern the nation. It represents the people through elected members of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, debating and passing bills that become law. This body also oversees the executive, ensuring accountability, which is vital for a functioning democracy.
- Describe the role of the executive. Answer: The executive, led by the Prime Minister and Council of Ministers, implements laws passed by the legislature. It handles daily administration, manages policies, and runs government departments, keeping the nation operational. In India, this branch works under the President but is driven by the elected government, ensuring democratic control.
- How does the judiciary contribute to democracy? Answer: The judiciary, headed by the Supreme Court, interprets laws and resolves disputes, acting as a guardian of justice. It checks the legislature and executive through judicial review, ensuring they stay within legal bounds, like striking down unfair laws. This role, seen in landmark cases, strengthens India’s democratic framework.
- Discuss the interconnection of institutions. Answer: The legislature creates laws, the executive puts them into action, and the judiciary ensures they’re legally sound, forming a connected system. This balance prevents overreach, as seen when the Supreme Court reviews executive decisions or Parliament amends laws. Such interplay, unique to India’s setup, supports a robust democracy.
6. Source-Based / Case-Based Assessment Questions
Source Extract: (Overview) “Rulers have to work with and within institutions in a democracy.”
Questions:
- Who works within institutions?
- Why needed?
- Example institution?
- Democratic benefit?
- Impact?
Answer Key:
- Rulers.
- Balance power.
- Legislature.
- Prevents autocracy.
- Stable governance.
Source Extract: (Legislature) “Parliament makes laws and represents people in India.”
Questions:
- What does Parliament do?
- Who is represented?
- Key body?
- Role in democracy?
- Example law?
Answer Key:
- Makes laws.
- People.
- Lok Sabha.
- Ensures voice.
- Citizenship Act.
Source Extract: (Judiciary) “Supreme Court resolves disputes and checks other branches.”
Questions:
- Who resolves disputes?
- What does it check?
- Key court?
- Democratic role?
- Example case?
Answer Key:
- Supreme Court.
- Legislature, executive.
- Supreme Court.
- Upholds justice.
- Kesavananda Bharati.
7. Solved Exercise-End Questions (NCERT Solutions)
- What are institutions? Answer: Institutions are governance structures like legislature, executive, judiciary. They manage democratic processes.
- Why are they needed? Answer: Ensure rulers follow rules, balance power. Prevent misuse in democracy.
- What does the legislature do? Answer: Makes laws, represents people. India’s Parliament is the key body.
- Role of the executive? Answer: Implements laws, runs administration. Led by the Prime Minister.
- Judiciary’s task? Answer: Resolves disputes, interprets laws. Supreme Court leads.
- How are they connected? Answer: Legislature makes, executive implements, judiciary checks. Forms a balanced system.
- What makes it democratic? Answer: Transparency, accountability, public role. Avoids autocratic tendencies.
- Central Government focus? Answer: Handles defense, foreign policy. Oversees national matters.
- State institution example? Answer: State legislature, led by Chief Minister. Manages local issues.
- Difference from US? Answer: US has stronger states, India central focus. Reflects federal variation.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, Working of Institutions Class 9 emphasizes that strong, well-functioning institutions are crucial for sustaining democracy. This chapter helps students understand how the legislature, executive, and judiciary maintain checks and balances, ensure accountability, and protect citizens’ rights. By learning about the working of institutions, students realize that democracy depends not just on elections, but on the effective functioning of these key pillars of governance.