🌟 Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) helps machines perform tasks that require human intelligence — understanding language, analyzing data, and even recognizing images.
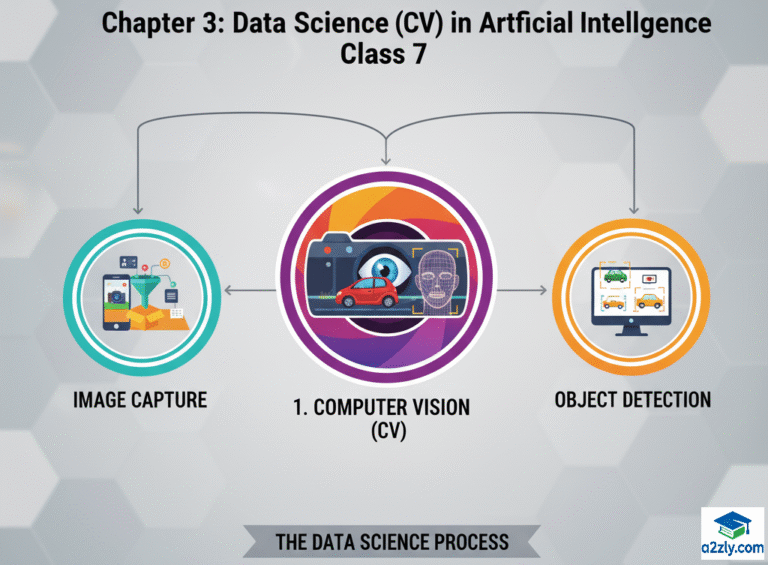
One of the most fascinating areas of AI is Computer Vision (CV) — the field that enables computers to “see” and interpret images and videos.
💡 Focus Keyword: Computer Vision in Artificial Intelligence Class 7 teaches students how computers process visual information, recognize patterns, and make smart decisions based on what they “see.”
From facial recognition in smartphones to traffic monitoring cameras, Computer Vision is the invisible eye of technology — transforming industries, safety, healthcare, and entertainment.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
📘 3.1 Introduction to Computer Vision
Computer Vision (CV) is a branch of Artificial Intelligence that enables machines to see, identify, and process images just like humans.
However, while humans use eyes and brains to recognize faces or objects, computers use cameras and algorithms to capture, process, and analyze visual data.
🧠 Definition:
Computer Vision is the science that allows computers to gain understanding from digital images or videos, interpret them, and make decisions based on that information.
🎯 Objective of Computer Vision:
- To help machines analyze visual content
- To enable decision-making through visuals
- To automate tasks requiring sight — such as detecting faces, identifying traffic signs, or diagnosing medical scans
💬 Example:
When your phone camera automatically detects faces and focuses, it’s using Computer Vision.
📘 Figure 3.1 – Human Vision vs. Computer Vision
+-----------------+ +--------------------------+
| Human Vision | | Computer Vision |
+-----------------+ +--------------------------+
| Eyes capture | | Camera captures images |
| images | | and videos |
| Brain interprets| | Algorithms interpret |
| and recognizes | | and classify objects |
+-----------------+ +--------------------------+
Alt Text: Computer Vision in Artificial Intelligence Class 7 – Comparison between human and computer vision.
🧩 3.2 What Is Computer Vision in AI?
Computer Vision is how AI systems interpret visual information to identify patterns and make sense of the environment.
It’s used in almost every modern innovation — face unlock, object detection, surveillance cameras, autonomous vehicles, and even social media filters.
🔹 How It Works Conceptually:
Computers break down an image into small units called pixels.
These pixels are analyzed using algorithms to detect shapes, colors, and textures. The AI model then compares this information to its training data to identify what’s in the image.
📊 Example:
A self-driving car’s AI camera captures a street image → detects red light → understands “stop” → sends command to brake system.
💡 Thus, Computer Vision gives machines the power to see, think, and act.
⚙️ 3.3 How Computer Vision Works in Artificial Intelligence
The process of Computer Vision in AI happens through four main stages:
🖼️ Step 1: Image Acquisition
- The computer captures images or videos using cameras or sensors.
- These images are converted into digital form for analysis.
📷 Example: CCTV cameras capturing live traffic footage.
🧩 Step 2: Feature Extraction
- The AI identifies important elements (features) in the image like edges, colors, or shapes.
- It focuses only on the necessary parts, like a face, object, or symbol.
💡 Example: Detecting eyes, nose, and mouth in facial recognition systems.
🔍 Step 3: Classification
- The AI compares the features detected with known categories stored in its database.
- It “classifies” what it sees — for instance, identifying whether the object is a car, animal, or person.
💡 Example: AI classifies an image as “cat” or “dog” after comparing it to stored images.
🤖 Step 4: Decision-Making
- Once the object is classified, the AI makes a decision or takes an action.
💡 Example:
In self-driving cars — if a pedestrian is detected, the AI decides to apply brakes.
📘 Figure 3.2 – Steps in Computer Vision
[ Image Acquisition ] → [ Feature Extraction ] → [ Classification ] → [ Decision Making ]
Alt Text: Steps in Computer Vision in Artificial Intelligence Class 7.
🌍 Real-Life Example – How Google Lens Works
When you scan a flower with Google Lens, it:
- Captures the image (acquisition)
- Detects its shape and color (feature extraction)
- Compares it with its database (classification)
- Displays the flower name (decision/action)
🏞️ 3.4 Examples of Computer Vision in Action
Computer Vision is a part of your daily life — often working silently behind the scenes.
Here are some exciting examples of Computer Vision in Artificial Intelligence Class 7:
📸 1. Facial Recognition
Used in smartphones, security systems, and attendance apps to identify people based on facial features.
🚗 2. Self-Driving Cars
Autonomous vehicles use cameras and sensors to detect pedestrians, traffic lights, and other vehicles.
🏥 3. Medical Imaging
AI detects diseases by analyzing X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans, helping doctors diagnose faster.
🌾 4. Smart Agriculture
Drones and cameras monitor crop growth, detect pests, and optimize watering schedules.
🔒 5. Surveillance & Security
AI-powered cameras detect unusual activities or intruders in real time.
🎮 6. Augmented Reality (AR)
Games like Pokémon GO use Computer Vision to identify real-world surfaces and objects.
📘 Figure 3.3 – Applications of Computer Vision
+--------------------+---------------------+-------------------+
| Facial Recognition | Self-Driving Cars | Medical Imaging |
| (Security) | (Transportation) | (Healthcare) |
+--------------------+---------------------+-------------------+
| Smart Agriculture | Surveillance System | Augmented Reality |
| (Farming) | (Safety) | (Gaming) |
+--------------------+---------------------+-------------------+
Alt Text: Applications of Computer Vision in Artificial Intelligence Class 7.
🌍 3.5 Importance of Computer Vision in Artificial Intelligence
Computer Vision is more than just a technological marvel — it is transforming industries globally.
Here’s why it’s crucial in the modern world:
🌾 1. Agriculture
- Monitors crop health using drone cameras.
- Detects diseases early to prevent yield loss.
- Reduces water and pesticide usage.
💡 Example: Smart irrigation systems using CV to assess soil conditions.
🛡️ 2. Security & Surveillance
- Detects unauthorized access or unusual behavior.
- Recognizes faces in large crowds for safety.
- Used in smart cities and airports.
💡 Example: AI cameras in schools for attendance and safety monitoring.
🚗 3. Transportation
- Self-driving vehicles use Computer Vision for navigation.
- Detects traffic signs and avoids collisions.
- Manages smart traffic control in cities.
💡 Example: AI systems adjusting traffic lights to reduce congestion.
🏥 4. Healthcare
- Analyzes scans for early disease detection.
- Tracks patient conditions using video data.
- Helps surgeons in precision operations.
💡 Example: AI diagnosing lung infections from X-rays.
🏭 5. Industry & Manufacturing
- Inspects products for defects on assembly lines.
- Tracks packaging quality and accuracy.
- Automates repetitive visual inspections.
💡 Example: AI ensuring that only perfect bottles are packed in a factory.
🎯 Why It Matters for Students
Learning Computer Vision in Artificial Intelligence Class 7 helps students:
- Think visually and logically.
- Understand how AI interacts with the physical world.
- Build real-world AI projects using images or videos.
🎮 3.6 Games That Use Computer Vision
Learning through play makes AI concepts easier to grasp.
Many interactive games and classroom activities are based on Computer Vision technology.
🕹️ 1. Teachable Machine (by Google)
- Students can train an AI to recognize gestures, faces, or colors using a webcam.
- Encourages creativity and experimentation.
💡 Example: Creating a hand-gesture recognition game using Google Teachable Machine.
🎲 2. Quick, Draw!
- An online game by Google AI that asks users to draw objects.
- The AI tries to guess the object using its Computer Vision model.
💡 Learning Outcome: Teaches how AI learns patterns and improves accuracy.
🤖 3. Kinect Sports / AR Games
- Use motion sensors to track player movement.
- Demonstrate real-time Computer Vision in action.
💡 Example: Jumping or running in a game is tracked using Computer Vision cameras.
🎨 4. AI Art and Drawing Games
- CV-based apps recognize sketches and color them automatically.
- Helps children understand how AI “sees” creativity.
💡 Example: AI predicting what a child is drawing and completing it.
📘 Classroom Activity: “AI Vision Lab”
Goal: Demonstrate Computer Vision in action.
Steps:
- Use webcam-based apps (like Teachable Machine).
- Train AI to recognize different colored objects.
- Test how accurately the AI identifies them.
💡 Skills Gained: Observation, creativity, and systems thinking.
🌱 Connecting Computer Vision to Sustainability
Computer Vision plays a huge role in achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
| SDG | AI Application | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 🌾 Zero Hunger (SDG 2) | Detecting crop health | Increases food productivity. |
| 🏙 Sustainable Cities (SDG 11) | Smart surveillance | Improves city safety. |
| 🌡 Climate Action (SDG 13) | Environmental monitoring | Tracks deforestation and pollution. |
| 🏥 Good Health (SDG 3) | Medical imaging | Improves healthcare accuracy. |
💡 Example: AI cameras identifying plastic waste for recycling contribute to SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption).
🧭 Recap of Chapter 3: Computer Vision in Artificial Intelligence Class 7
- Computer Vision helps machines understand visual data.
- It works through image acquisition → feature extraction → classification → decision-making.
- Applications span across security, healthcare, transport, and gaming.
- Supports sustainability and SDGs through smart visual systems.
- Encourages creativity and practical learning among students.
🧩 Exercise Section
🌟 1. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Choose the correct option.
- Computer Vision enables machines to —
A. Understand spoken language
B. See and interpret images or videos
C. Play musical instruments
D. Store large data
Answer: B - Which of the following best defines Computer Vision?
A. Making machines speak
B. Teaching computers to understand pictures and videos
C. Storing numerical data
D. Converting speech to text
Answer: B - In Computer Vision, visual data is captured using —
A. Sensors only
B. Cameras and sensors
C. Keyboards
D. Voice assistants
Answer: B - Which of these steps is NOT part of the Computer Vision process?
A. Image Acquisition
B. Feature Extraction
C. Classification
D. Audio Processing
Answer: D - What does “Feature Extraction” mean in Computer Vision?
A. Storing text information
B. Identifying shapes, edges, and colors in an image
C. Translating text into another language
D. Sorting files
Answer: B - When your phone recognizes your face, it uses —
A. Data Science
B. Computer Vision
C. Natural Language Processing
D. Robotics
Answer: B - Which real-life application uses Computer Vision?
A. Google Translate
B. Self-Driving Cars
C. Music Apps
D. Email Filters
Answer: B - In AI systems, pixels represent —
A. Units of visual data in images
B. Text characters
C. Sound signals
D. Numbers in spreadsheets
Answer: A - Which Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) is supported by Computer Vision in agriculture?
A. Quality Education (SDG 4)
B. Zero Hunger (SDG 2)
C. Climate Action (SDG 13)
D. Industry and Innovation (SDG 9)
Answer: B - What happens in the “Decision-Making” stage of Computer Vision?
A. The AI deletes images
B. The AI makes an action based on identified visuals
C. The AI collects more pictures
D. The AI ignores unrecognized data
Answer: B
✅ Answer Key (MCQs)
1-B | 2-B | 3-B | 4-D | 5-B | 6-B | 7-B | 8-A | 9-B | 10-B
✍️ 2. Fill in the Blanks
- Computer Vision enables machines to __________ and understand images.
Answer: see - In humans, eyes capture images, but in AI, __________ capture visuals.
Answer: cameras - Computer Vision works by analyzing small units of images called __________.
Answer: pixels - The process of finding shapes, colors, and edges is called __________.
Answer: feature extraction - In the classification stage, AI compares images with its __________.
Answer: database - When a pedestrian is detected, a self-driving car decides to __________.
Answer: apply brakes - AI in medical imaging helps detect __________ early.
Answer: diseases - Games like Pokémon GO use __________ Reality and Computer Vision.
Answer: Augmented - The AI tool that can identify objects you draw is __________.
Answer: Quick, Draw! - Computer Vision supports SDG 11 by creating __________ cities.
Answer: sustainable or smart
⚖️ 3. Assertion–Reason Questions
Choose the correct option:
A — Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation.
B — Both are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation.
C — Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
D — Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
- Assertion: Computer Vision enables AI systems to analyze images.
Reason: It helps machines understand spoken commands.
Answer: C - Assertion: In Computer Vision, cameras act as the system’s eyes.
Reason: They capture visual data for AI to interpret.
Answer: A - Assertion: Feature extraction helps AI detect important parts of an image.
Reason: It focuses only on irrelevant areas.
Answer: C - Assertion: Computer Vision contributes to sustainability.
Reason: It monitors crops, pollution, and energy use through visual systems.
Answer: A - Assertion: Self-driving cars use Computer Vision for navigation.
Reason: CV helps them identify traffic signals and pedestrians.
Answer: A
💬 4. Very Short Answer Type Questions (VSAQs)
(Answer in 1–2 lines)
- What is Computer Vision?
Answer: A branch of AI that enables machines to see, understand, and interpret images or videos. - How is human vision different from computer vision?
Answer: Humans use eyes and brains, while computers use cameras and algorithms. - List any two stages of the Computer Vision process.
Answer: Image Acquisition and Feature Extraction. - Define Image Acquisition.
Answer: The process of capturing images or videos using cameras or sensors. - What happens in Feature Extraction?
Answer: AI detects shapes, edges, and patterns within images. - Give one example of Computer Vision in healthcare.
Answer: AI analyzing X-rays to detect diseases. - Name one Computer Vision-based game.
Answer: Quick, Draw! - What is the main purpose of classification in Computer Vision?
Answer: To identify and categorize objects in images. - Which SDG is achieved through Smart Agriculture using CV?
Answer: Zero Hunger (SDG 2). - Give one real-life use of CV in transportation.
Answer: Self-driving cars detecting road signs.
🧩 5. Short Answer Type Questions (SAQs)
(Answer in 2–3 sentences)
- Explain how Computer Vision works in AI.
Answer: It captures images, extracts features, classifies them, and takes action based on what it identifies — just like human sight but through algorithms. - What are the four main stages of the Computer Vision process?
Answer: Image Acquisition, Feature Extraction, Classification, and Decision-Making. - How does Computer Vision help in agriculture?
Answer: It monitors crop growth, detects pests, and supports sustainable farming using drone images. - Describe the importance of Feature Extraction.
Answer: It allows AI to focus on key details, such as edges or patterns, which are crucial for recognizing objects accurately. - Give two examples of Computer Vision in everyday life.
Answer: Face unlock in smartphones and surveillance cameras in cities. - What is classification in Computer Vision?
Answer: The step where AI identifies what an image represents by comparing it to stored data. - Mention one use of CV in healthcare and explain briefly.
Answer: AI scans medical images like X-rays to detect early signs of illness, helping doctors diagnose faster. - How is CV used in traffic systems?
Answer: Cameras detect vehicles, monitor signals, and help manage traffic flow efficiently. - What is the role of Decision-Making in CV?
Answer: After identifying an object, AI decides what action to take, such as stopping a vehicle or triggering an alert. - Why is learning Computer Vision important for students?
Answer: It encourages logical thinking, creativity, and understanding of real-world AI applications.
🧠 6. Long Answer Type Questions (LAQs)
(Answer in 5–8 sentences)
- Define Computer Vision and explain how it works in Artificial Intelligence.
Answer: Computer Vision is an AI field that allows machines to interpret visual data. It involves capturing images (acquisition), identifying features (extraction), classifying objects, and taking action. For example, self-driving cars use CV to detect traffic signs and pedestrians. It helps machines “see” and make decisions like humans. - Discuss the importance of Computer Vision in daily life.
Answer: CV powers technologies like face unlock, medical imaging, traffic monitoring, and augmented reality. It enhances safety, convenience, and efficiency across industries. From diagnosing diseases to improving road safety, it’s shaping the future of automation. - Explain the stages of the Computer Vision process with examples.
Answer: The process includes:- Image Acquisition: Cameras capture visuals.
- Feature Extraction: AI identifies shapes and edges.
- Classification: The system matches data with known images.
- Decision-Making: It takes action, like stopping a car.
Example: Google Lens uses these steps to identify objects.
- How does Computer Vision contribute to sustainability and SDGs?
Answer: It supports SDGs like Zero Hunger, Good Health, and Sustainable Cities by monitoring crops, improving healthcare, and tracking pollution. For instance, AI drones help detect deforestation, aiding environmental protection. - Describe how Computer Vision is used in games and education.
Answer: Games like Teachable Machine and Quick, Draw! teach students how AI recognizes patterns and learns visually. These activities make learning engaging and build skills in creativity, data analysis, and systems thinking.
🌍 7. Source-Based / Case-Based Assessment Questions
Case Study 1: Smart Traffic Management
Source Extract:
“Modern cities use AI-based Computer Vision cameras to monitor roads. The system detects traffic density, reads signal patterns, and adjusts green light durations automatically. This reduces congestion and saves fuel.”
Questions:
- Which AI technology is used in this system?
- How does Computer Vision help reduce congestion?
- Mention one sustainability benefit of this innovation.
- Identify the SDG supported by this system.
Answer Key:
- Computer Vision.
- By analyzing vehicle flow and controlling signals intelligently.
- Saves fuel and reduces pollution.
- Sustainable Cities and Communities (SDG 11).
Case Study 2: Computer Vision in Healthcare
Source Extract:
“AI models trained on thousands of X-rays can now detect lung infections within seconds. Doctors use these results for quick diagnosis and treatment decisions.”
Questions:
- What role does Computer Vision play here?
- How does it benefit doctors and patients?
- Mention one challenge in using CV for healthcare.
- Which SDG goal does this align with?
Answer Key:
- It analyzes medical images to detect diseases.
- Provides faster and more accurate diagnoses.
- Data privacy and image accuracy issues.
- Good Health and Well-Being (SDG 3).
Case Study 3: Smart Farming with Drones
Source Extract:
“Farmers use drone cameras powered by Computer Vision to monitor crop growth and detect pests early. The data helps reduce pesticide use and improve crop yield.”
Questions:
- What type of AI system is being used?
- How does it promote sustainable agriculture?
- Which data is analyzed by the system?
- Identify the SDG related to this case.
Answer Key:
- Computer Vision with AI-powered drones.
- It minimizes chemical use and saves resources.
- Visual data from crops and fields.
- Zero Hunger (SDG 2).
Case Study 4: AI in Education – Smart Attendance System
Source Extract:
“Schools are using facial recognition-based attendance systems. Cameras identify each student’s face and mark attendance automatically, saving time for teachers.”
Questions:
- Which AI domain powers this system?
- How does it simplify administrative work?
- Mention one ethical concern of such systems.
- Suggest one improvement to ensure privacy.
Answer Key:
- Computer Vision.
- Automates attendance tracking efficiently.
- Privacy and data misuse concerns.
- Use encrypted data storage and consent-based use.
❓ FAQ – Computer Vision in Artificial Intelligence Class 7
Q1. What is Computer Vision?
👉 It is the branch of AI that allows machines to see, analyze, and make sense of images and videos.
Q2. How does Computer Vision work?
👉 It follows steps like image acquisition, feature extraction, classification, and decision-making.
Q3. Where is Computer Vision used?
👉 In face recognition, self-driving cars, surveillance, and medical imaging.
Q4. What tools can students use to learn Computer Vision?
👉 Google Teachable Machine, Quick Draw, and AI-based educational games.
Q5. Why is Computer Vision important?
👉 It improves safety, healthcare, automation, and supports sustainable living.
🔗 Internal Links
- Domains of AI – Class 7 Chapter 1
- Data Science in AI – Class 7 Chapter 2
- Digital Citizenship and AI Ethics – Class 7 Chapter 5
🌍 External DoFollow Sources
🏁 Conclusion
The world is full of images — and through Computer Vision in Artificial Intelligence Class 7, students learn how machines interpret them.
From identifying objects to helping doctors, Computer Vision merges technology with creativity and empathy.
By understanding how AI sees, students develop not just technical knowledge but ethical awareness — using AI for good, sustainability, and social progress.
Computer Vision isn’t just about teaching machines to see —
👁️ It’s about teaching humans to look deeper into the future.