🧭 Chapter Overview
AI systems make decisions based on data.
But if that data is incomplete, unbalanced, or unfair, the AI can learn bias — leading to unfair, incorrect, or discriminatory outcomes.
This chapter helps us understand what AI bias is, how it occurs, and how to reduce it to make AI more ethical and responsible.
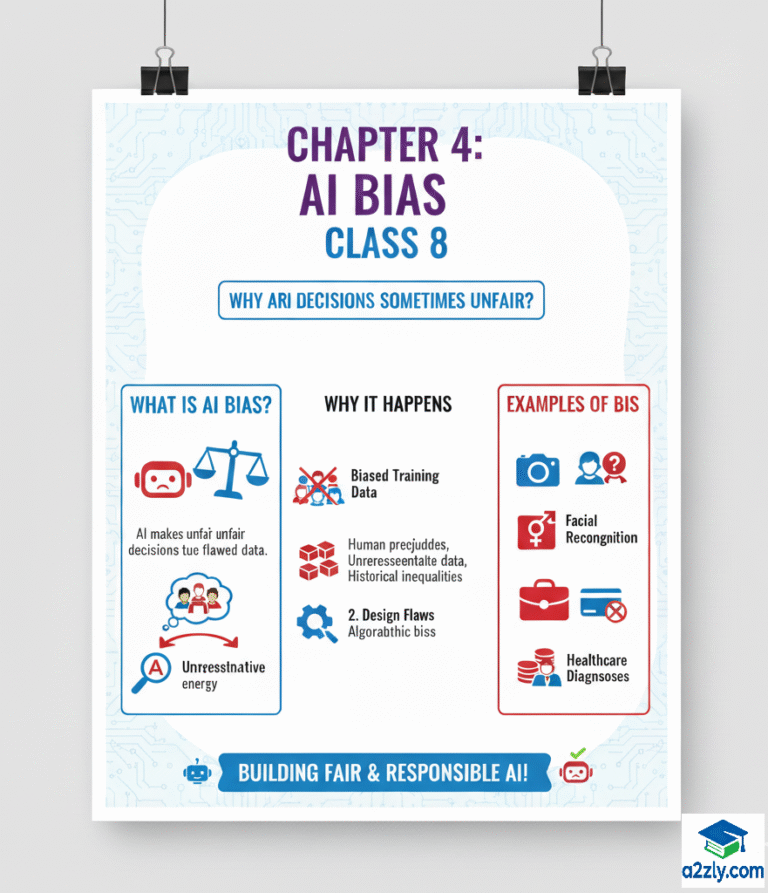
4.1 Introduction to AI Bias
💡 Definition:
AI Bias means the unfair or prejudiced behavior shown by an AI system because of biased data, design, or human influence.
It happens when AI makes unequal judgments or decisions that favor one group over another.
🧩 Example:
- A facial recognition system works better on men than women → biased AI.
- A hiring AI tool that prefers men over women because it was trained on biased data → biased AI.
📖 In Simple Words:
AI bias is like teaching a student with only one kind of example — they will perform poorly on new or different examples.
🧠 Mind Map: Introduction to AI Bias
AI BIAS
|
-----------------------------
| | |
Causes Effects Prevention
(Data) (Unfairness) (Ethics, Checks)
4.2 How Does AI Learn?
To understand bias, we first need to know how AI learns.
⚙️ AI Learning Process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Data Collection | AI collects data from different sources |
| 2️⃣ Data Training | AI model learns patterns from this data |
| 3️⃣ Prediction | AI uses learned patterns to make decisions |
| 4️⃣ Feedback | The results are checked and improved |
🧩 Example:
If an AI is trained only on pictures of white cats, it may not recognize black cats later — because it learned from a limited dataset.
🧠 Mind Map: How AI Learns
How AI Learns
|
-----------------------
| | |
Data Training Output
Collect Process Prediction
4.3 How Bias Occurs in AI
Bias can appear anywhere in the AI lifecycle, from data collection to deployment.
⚙️ Main Causes of Bias in AI:
| Stage | Cause of Bias | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Non-diverse or incorrect data | AI trained only on photos of adults, not children |
| Data Labeling | Human error while labeling | Mislabeling images as wrong categories |
| Model Training | Learning from biased patterns | AI prefers one group because data is unbalanced |
| Algorithm Design | Biased rules or logic | Algorithm written with wrong assumptions |
| Feedback Loop | Bias reinforced over time | Search engines showing biased results repeatedly |
🧠 Mind Map: How Bias Occurs
How AI Bias Occurs
|
--------------------------------
| | | |
Data Model Algorithm Feedback
Error Training Design Loop
4.4 Examples of AI Bias
| Area | Example | Type of Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Hiring | AI tool rejecting women’s resumes because training data favored men | Gender Bias |
| Healthcare | AI model trained mostly on white patients → misdiagnoses dark skin tones | Racial Bias |
| Voice Assistants | Struggle to understand certain accents | Language Bias |
| Law & Order | Facial recognition falsely identifying minority groups | Racial/Facial Bias |
| Education | AI grading essays better for specific writing styles | Cultural Bias |
🧩 Real-Life Case Study:
- Amazon Hiring AI (2018):
The system favored male candidates because it was trained on past hiring data — mostly men. - Apple Credit Card (2019):
AI gave men higher credit limits than women with the same income — due to biased data.
🧠 Mind Map: Examples of AI Bias
Examples of AI Bias
|
-----------------------------
| | | |
Hiring Healthcare Voice Education
4.5 Types of Bias
AI bias can come in different forms.
Here are the main types 👇
| Type of Bias | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Data Bias | When training data is unbalanced or incomplete | AI trained mostly on male faces |
| Algorithmic Bias | When algorithm design causes unfair outcomes | Wrong formula gives wrong priority |
| Prejudice Bias | When human beliefs or stereotypes affect AI | Gender or racial prejudice in data |
| Measurement Bias | When data collection tools are inaccurate | Faulty sensors collecting incorrect data |
| Label Bias | Wrong labeling of training data | Tagging all doctors as “he” |
| Confirmation Bias | AI reinforces existing beliefs | Recommending similar news repeatedly |
🧠 Mind Map: Types of AI Bias
Types of AI Bias
|
-------------------------------------
| | | | |
Data Algorithmic Label Measurement Prejudice
4.6 How We Can Reduce AI Bias
Bias cannot be removed completely, but it can be minimized through ethical and technical measures.
✅ Steps to Reduce AI Bias
| Step | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Use Diverse Data | Include data from all genders, ages, races | Balanced training datasets |
| 2️⃣ Human Oversight | Regularly review AI decisions | Manual audits |
| 3️⃣ Bias Testing | Test model outputs for fairness | Compare accuracy across groups |
| 4️⃣ Transparent Algorithms | Make AI logic understandable | Open-source coding |
| 5️⃣ Ethical AI Guidelines | Follow AI ethics frameworks | UNESCO or government policies |
💬 Tip:
Just like teachers check if exam questions are fair for all students, AI developers must check if models are fair for all users.
🧠 Mind Map: Reducing Bias
Reducing AI Bias
|
----------------------------
| | | |
Diverse Testing Oversight Ethics
Data
4.7 Ethical Challenges
AI bias raises ethical and moral questions that must be addressed responsibly.
⚖️ Major Ethical Challenges
| Challenge | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Fairness | Ensuring AI treats all groups equally | Equal job selection for men & women |
| Transparency | Understanding how AI makes decisions | Clear explanation of model logic |
| Accountability | Identifying who is responsible for biased outcomes | Developer or organization? |
| Privacy | Avoiding misuse of personal data | AI using user data without consent |
| Trust | Building user confidence in AI systems | Avoiding fake or misleading results |
🧩 Ethical AI Principles (UNESCO/UN):
- Fairness – Treat everyone equally.
- Accountability – Be responsible for AI’s decisions.
- Transparency – Be clear about how AI works.
- Privacy – Protect user data.
- Beneficence – Use AI for human good.
🧠 Mind Map: Ethical Challenges
Ethical Challenges in AI Bias
|
---------------------------------
| | | | |
Fairness Privacy Trust Transparency Accountability
📘 Summary Table: Chapter 4 – AI Bias
| Section | Topic | Key Idea |
|---|---|---|
| 4.1 | Introduction | AI Bias = unfair decisions due to data or design |
| 4.2 | How AI Learns | AI learns patterns from training data |
| 4.3 | How Bias Occurs | Bias enters through data, labeling, or algorithms |
| 4.4 | Examples | Seen in hiring, healthcare, and education |
| 4.5 | Types | Data, Algorithmic, Prejudice, Label, Measurement |
| 4.6 | Reducing Bias | Use diverse data, test fairness, follow ethics |
| 4.7 | Ethical Challenges | Fairness, accountability, privacy, trust |
✅ Key Takeaways
- AI Bias happens when AI makes unfair decisions due to biased data or design.
- Bias can occur at any stage — from data collection to deployment.
- There are many types — Data Bias, Algorithmic Bias, Label Bias, etc.
- Reducing bias needs diverse data, transparency, and human supervision.
- Ethical AI ensures fairness, privacy, accountability, and trust in technology.
🧠 Complete Chapter Mind Map
AI BIAS
|
-------------------------------------------------
| | | | | |
Intro Causes Examples Types Reduction Ethics
| | | | | |
Data Design Gender Data Diverse Fairness
Bias Error Bias Bias Data Privacy