🧭 Chapter Overview
Light plays a vital role in our daily life — from the reflection you see in a mirror every morning to the lenses in your spectacles or camera. This chapter, “Light: Mirrors and Lenses,” introduces you to the fascinating science of how light interacts with surfaces and materials.
You’ll learn about different mirrors (plane, concave, convex), how lenses bend light, and how real-world devices like car mirrors, eyeglasses, and telescopes work.
By the end of this lesson, you’ll see how physics and daily life beautifully reflect one another — quite literally!
Table of Contents
🪶Uses of Mirrors and Lenses in Daily Life
| Device | Type Used | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Shaving Mirror | Concave | Enlarges face for a close shave |
| Vehicle Rear-view | Convex | Provides wider field of view |
| Dentist’s Mirror | Concave | Enlarged image of teeth |
| Magnifying Glass | Convex | Enlarges text or objects |
| Spectacles | Concave/Convex | Correct vision |
| Telescope | Concave Mirror + Convex Lens | View distant objects |
| Camera Lens | Convex | Focuses light to form image |
1️⃣ INTRODUCTION: WHY THIS CHAPTER IS IMPORTANT
Light helps us see objects.
When light strikes a surface, it may:
- Reflect (bounce back)
- Pass through (as in lenses)
Earlier, we studied plane mirrors, which form simple images.
But curved mirrors and lenses can:
- Change image size
- Change image position
- Change image orientation
This chapter explains how and why.
2️⃣ SPHERICAL MIRRORS
🔹 Definition
A spherical mirror is a mirror whose reflecting surface is curved and forms a part of an imaginary hollow sphere.
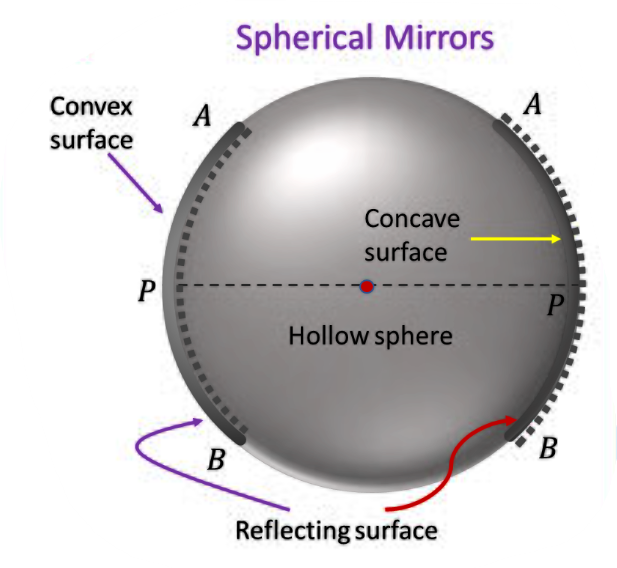
🔹 Types of Spherical Mirrors
(A) CONCAVE MIRROR
- Reflecting surface curves inward
- Known as a converging mirror
- Can form erect or inverted images
📌 Key Property:
Parallel rays converge after reflection.
(B) CONVEX MIRROR
- Reflecting surface bulges outward
- Known as a diverging mirror
- Always forms erect and diminished images
📌 Key Property:
Parallel rays diverge after reflection.
🔍 HOW THEY ARE MADE
- Flat glass is ground and polished
- Reflective coating:
- Outer surface → Concave mirror
- Inner surface → Convex mirror
3️⃣ IMAGE FORMATION BY SPHERICAL MIRRORS
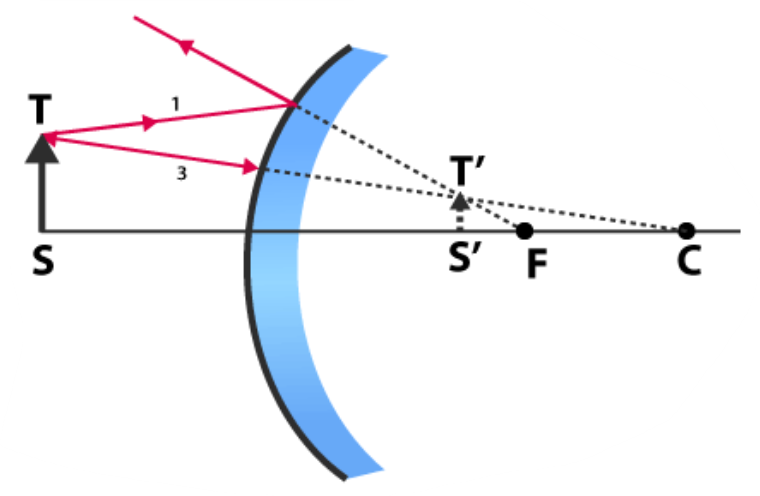
🔶 IMAGE BY A CONCAVE MIRROR

| Object Position | Image Nature |
|---|---|
| Very close | Erect & enlarged |
| Farther away | Inverted |
| Size | Changes continuously |
📌 Conclusion (EXAM LINE):
A concave mirror can form enlarged, diminished, erect, or inverted images depending on object distance.
🔶 IMAGE BY A CONVEX MIRROR
| Property | Observation |
|---|---|
| Nature | Always erect |
| Size | Always diminished |
| Position | Behind the mirror |
📌 Conclusion:
A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image.
🔁 COMPARISON TABLE
| Mirror | Image Size | Orientation |
|---|---|---|
| Plane | Same | Erect |
| Concave | Changes | Erect / Inverted |
| Convex | Smaller | Always erect |
4️⃣ USES OF MIRRORS IN DAILY LIFE

✅ Uses of Concave Mirror
- Torch & vehicle headlights (to focus light)
- Dentist mirror (enlarged image)
- Solar furnaces
- Reflecting telescopes
✅ Uses of Convex Mirror
- Side-view mirrors of vehicles
- Road intersections
- Shopping malls for surveillance
⚠️ Why warning on vehicles?
👉 “Objects in mirror are closer than they appear”
Because convex mirrors make images smaller and farther.
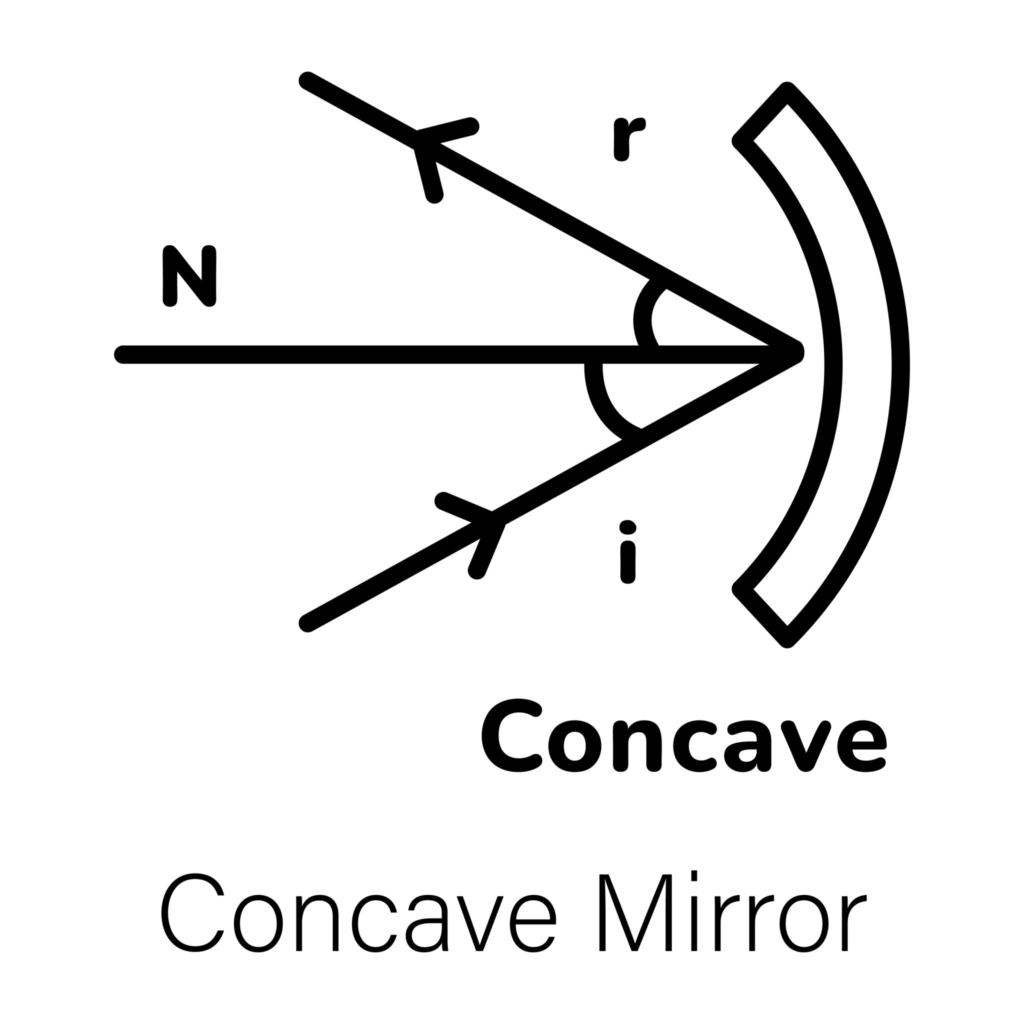
5️⃣ LAWS OF REFLECTION (VERY IMPORTANT)


🔹 Law 1
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
🔹 Law 2
Incident ray, reflected ray, and normal lie in the same plane
📐 IMPORTANT TERMS
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Incident ray | Ray falling on mirror |
| Reflected ray | Ray bouncing back |
| Normal | Perpendicular at point of incidence |
| Angle of incidence | Between incident ray & normal |
| Angle of reflection | Between reflected ray & normal |
📌 If light falls along the normal → both angles = 0°
6️⃣ REFLECTION OF PARALLEL RAYS



| Mirror | Behaviour |
|---|---|
| Plane mirror | Rays remain parallel |
| Concave mirror | Rays converge |
| Convex mirror | Rays diverge |
📌 Exam Point:
Laws of reflection are valid for all mirrors, including spherical mirrors.
7️⃣ CONCENTRATION OF SUNLIGHT


- Concave mirrors focus sunlight at one point
- Produces high temperature
- Can burn paper
Applications
- Solar cookers
- Solar furnaces
- Power generation
⚠️ Safety Rule:
Never look directly at the Sun or reflected sunlight.
8️⃣ LENSES


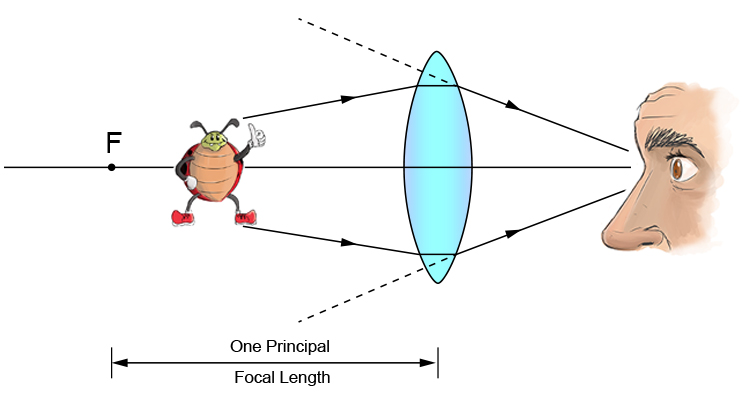
🔹 Definition
A lens is a transparent material (glass/plastic) having at least one curved surface that refracts light.
9️⃣ TYPES OF LENSES
(A) CONVEX LENS
- Thicker at centre
- Thinner at edges
- Converges light
- Also called converging lens
(B) CONCAVE LENS
- Thinner at centre
- Thicker at edges
- Diverges light
- Also called diverging lens
🔟 IMAGE FORMATION BY LENSES



Convex Lens
- Near object → Erect & enlarged
- Far object → Inverted
- Size changes with distance
Concave Lens
- Always erect
- Always diminished
1️⃣1️⃣ CONVERGENCE & DIVERGENCE BY LENSES
| Object | Effect on Light |
|---|---|
| Glass plate | No change |
| Convex lens | Converges |
| Concave lens | Diverges |
Convex lens can also burn paper by concentrating sunlight.
1️⃣2️⃣ USES OF LENSES


4
- Spectacles
- Cameras
- Microscopes
- Telescopes
- Smartphone cameras
- Human eye (flexible convex lens)
1️⃣3️⃣ IMPORTANT EXPLANATION
Pencil in Water Appears Bent – Why?
Because light changes direction (refraction) when it moves from air to water.
1️⃣4️⃣ QUICK REVISION (EXAM READY)
- Concave mirror → converges light
- Convex mirror → diverges light
- Convex lens → converges light
- Concave lens → diverges light
- Convex mirrors preferred for vehicles (wide view)
- Laws of reflection apply to all mirrors
🧬 Our Scientific Heritage
Over 800 years ago, Indian astronomers during Bhāskara II’s era used reflection from water surfaces to measure star positions.
Even without written laws, their instruments reflected an advanced understanding of optics — proof that ancient India contributed deeply to light science.
🔗 INTERNAL & EXTERNAL LINKS
Internal Links (A2ZLY):
- Chapter 9 – The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions Notes 2025
- Class 8 Science All Chapters Smart Notes (NEP 2025 Edition)
- Smart Notes Creator NEP 2025 Hub | A2ZLY
External Links: