1️⃣ Chapter Overview
🎓 What this chapter teaches us:
Nature is like a perfect orchestra 🎶—every living and non-living part plays its role to keep life balanced.
🔑 Core Ideas at a Glance:
- 🌱 Habitat = place to live + food + water + shelter
- 🧬 Biotic (living) & 🌬️ Abiotic (non-living) parts work together
- 👨👩👧👦 Same species → Population | Different species → Community
- 🌍 Community + abiotic environment → Ecosystem
- 🔗 Energy flows through food chains & food webs
- ♻️ Waste is recycled by decomposers
- ⚠️ Human activities can disturb balance
- 🌿 Conservation = key to a sustainable future
✨ By the end, you’ll clearly understand how nature maintains harmony and why protecting it protects us.
2️⃣ Complete Concept-Wise Explanation
🐘 Introduction: Why Elephants Enter Human Areas
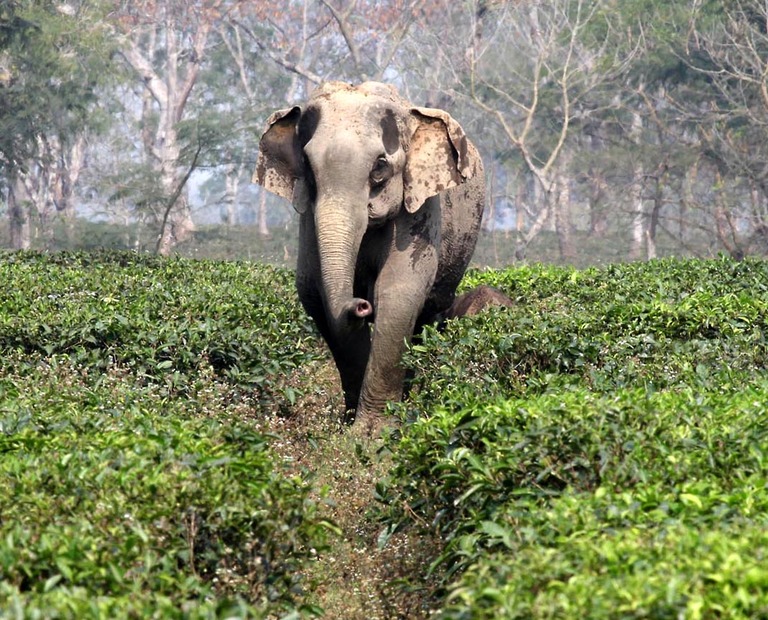


🐘 In states like Odisha, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Assam, Chhattisgarh, elephants often enter farms and villages.
❓ Why does this happen?
- 🌳 Deforestation → fewer trees
- 🌧️ Irregular rainfall → dry waterholes
- 🍃 Less vegetation → food shortage
👉 Elephants move towards banana, sugarcane, and rice fields 🌾 for survival.
✅ Solution: Elephant Corridors
- 🛣️ Protected forest paths
- 🔄 Connect forest patches
- 🛑 Reduce human–animal conflict
📌 Key Message:
A small change (cutting trees 🌳) → big effects (animal movement 🐘 → human problems).
🏡 12.1 Habitat – Our Natural Home
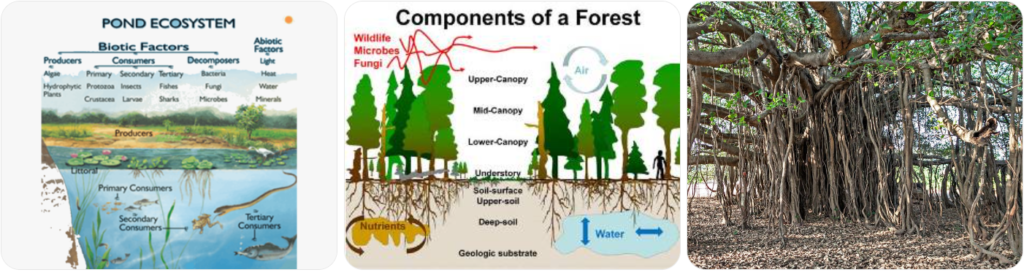
🏠 Habitat
The natural place where an organism gets:
- 🍽️ Food
- 💧 Water
- 🏡 Shelter
- 🌌 Space
🔹 Can be big (forest 🌳) or small (tree bark 🌱).
🧩 Components of a Habitat
| 🌱 Biotic (Living) | 🌬️ Abiotic (Non-living) |
|---|---|
| Plants, animals, microbes | Air, water, soil, sunlight, temperature |
📌 Example: Pond
- 🐟 Fish → get oxygen from water
- 🌿 Algae → make food
- 🐸 Frogs, 🦆 ducks, 🐌 snails → interact with each other
⏰ Time sharing helps coexistence:
- 🐍 Snake (night)
- 🐭 Rodent (day)
👥 12.2 Population & Community
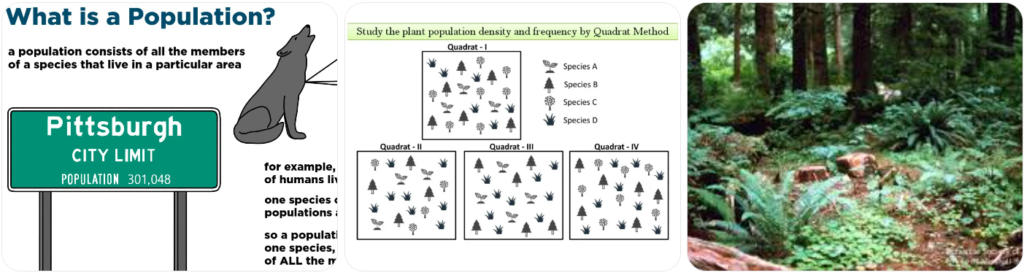
👤 Population
➡️ Same species + same place + same time
🧮 Example: All fish of one kind in a pond
👨👩👧👦 Community
➡️ Many different populations living together
🌼 Includes plants + animals + microorganisms
🌸 Ever Heard of Pollination?
- 🌺 Flowers need pollen transfer
- 🐝 Agents: insects, wind, water, birds, bats
- ✅ Leads to fruits & seeds
⚖️ 12.3 Does Every Organism Matter?

🧪 Two Ponds Study
| Pond A 🐟 | Pond B ❌ |
|---|---|
| Fish present | No fish |
| More flowers 🌼 | Fewer flowers |
🔗 Chain Reaction:
🐟 Fish → eat dragonfly larvae
🦟 Fewer dragonflies → 🐝 more pollinators
🌸 More pollination → more plants
📌 Lesson: Removing one organism can disturb the whole ecosystem.
🔄 12.4 Interactions in an Ecosystem
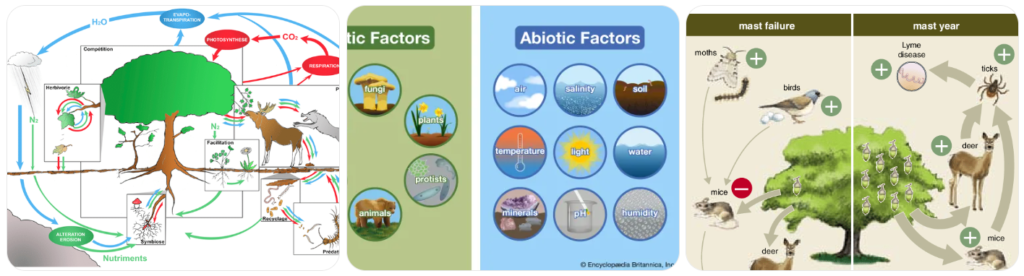
🔁 Types of Interactions
🔹 Biotic ↔ Abiotic
- 🌱 Plants need sunlight
- 🐟 Fish lay eggs in water
🔹 Abiotic ↔ Abiotic
- ☀️ Sunlight → high temperature
- 💧 Sun → evaporation
🔹 Biotic ↔ Biotic
- 🐸 Frog eats insects
- 🐍 Snake eats fish
- 🐸🐟 Competition for larvae
👉 All together = Ecosystem
🌍 Types of Ecosystems
- 💧 Aquatic – pond, lake, river
- 🌳 Terrestrial – forest, grassland
- 🚜 Human-made – farms, parks
🍽️ 12.5 Who Eats Whom?
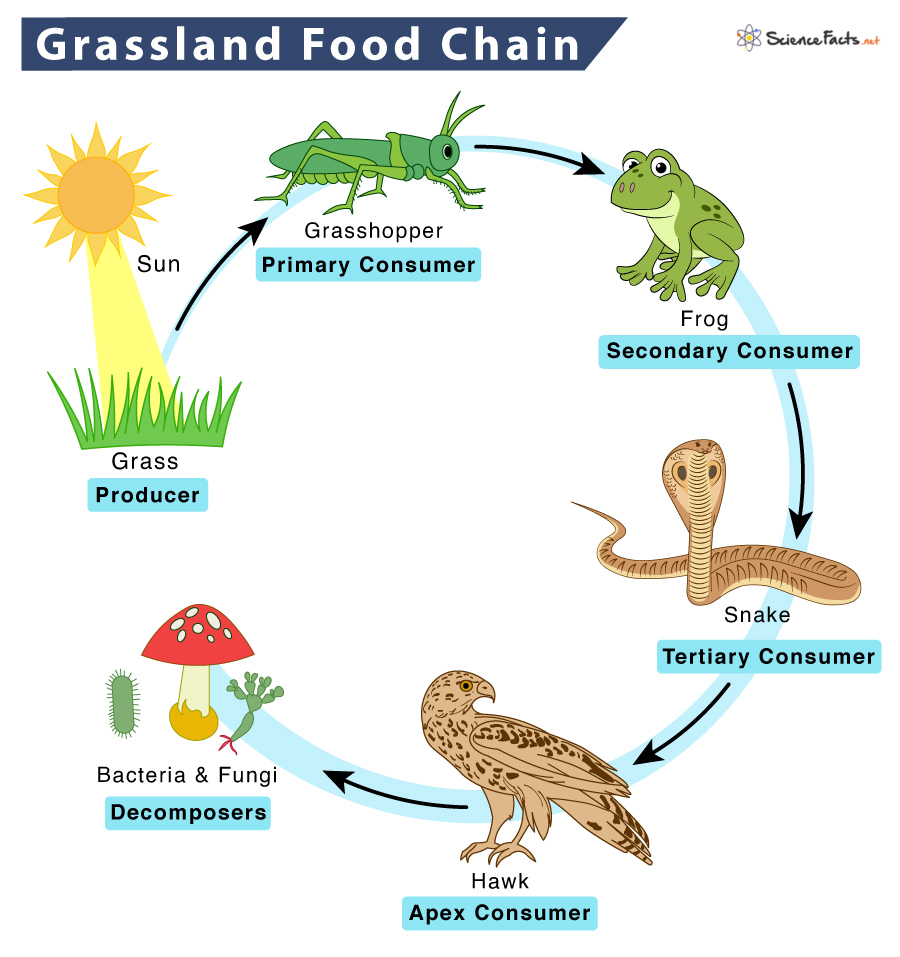
🌿 Producers (Autotrophs)
- Green plants 🌱
- Make food by photosynthesis
🐾 Consumers (Heterotrophs)
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| 🐄 Herbivores | Deer, hare |
| 🐅 Carnivores | Tiger, leopard |
| 🐦 Omnivores | Crow, fox |
🍄 Decomposers
- Fungi & bacteria
- Recycle nutrients ♻️
🔗 Food Chain
🌱 Grass → 🐰 Hare → 🦊 Fox
🌐 Food Web
Many food chains interconnected
♻️ 12.6 What Happens to Waste?
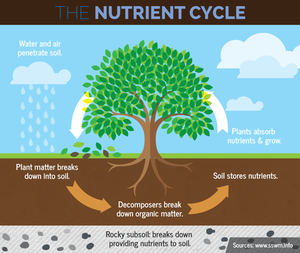
🍂 Dead plants + animals + waste
⬇️
🍄 Decomposers break them down
⬇️
🌱 Nutrients return to soil
📌 Nature wastes nothing!
🔁 12.7 One Change → Many Effects

⚠️ Example:
- Pollution → plants die
- Oxygen ↓ → fish die
- Insects ↑ → crops damaged
- Pesticides ↑ → more harm
🐸 1980s Frog Case (India):
- Frog export ↑
- Insects ↑
- Pesticides ↑
- Govt banned export → balance restored
🤝 12.8 Interactions that Maintain Balance
| Interaction | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 🤝 Mutualism | Both benefit | Bee 🐝 & flower 🌸 |
| 🪴 Commensalism | One benefits | Orchid on tree |
| 🦠 Parasitism | One harmed | Tick on dog |
🌿 12.9 Benefits of Ecosystems

🌍 Ecosystems provide:
- 🌬️ Clean air
- 💧 Fresh water
- 🍎 Food & medicines
- 🌦️ Climate control
- 🎒 Recreation
🌊 Sundarbans
- Protects coast from storms
- Absorbs CO₂
- UNESCO World Heritage Site
🚜 12.9.1 Human-Made Ecosystems
- Farms, parks, fish ponds
- Need human care
- Can support biodiversity if managed well 🌼
🌾 12.9.2 Ecosystems & Farming
⚙️ Green Revolution helped food production
❌ But caused:
- Soil degradation
- Loss of microbes
- Pest resistance
✅ Sustainable Solutions:
- Organic farming 🌱
- Natural manure (Kunapa Jala)
- Protect soil organisms 🪱
3️⃣ Important Definitions (Quick Revision)
🟢 Habitat:
- The natural place where an organism lives
- Provides food, water, shelter, and space
🟢 Biotic Components:
- All living organisms in a habitat
- Includes plants, animals, and microorganisms
🟢 Abiotic Components:
- All non-living parts of a habitat
- Air, water, soil, sunlight, temperature
🟢 Population:
- Group of individuals of the same species
- Living in the same habitat at a given time
🟢 Community:
- All the different populations of organisms
- Living and interacting in the same habitat
🟢 Ecosystem:
- A community of living organisms
- Plus the abiotic components they interact with
🟢 Producers / Autotrophs:
- Organisms that make their own food
- Mainly green plants using photosynthesis
🟢 Consumers / Heterotrophs:
- Organisms that cannot make food
- Depend on plants or animals for nutrition
🟢 Herbivores:
- Animals that eat only plants
🟢 Carnivores:
- Animals that eat only other animals
🟢 Omnivores:
- Animals that eat both plants and animals
🟢 Decomposers / Saprotrophs:
- Fungi and bacteria
- Break down dead matter and waste
- Recycle nutrients back into the soil
🟢 Food Chain:
- A linear sequence showing transfer of food energy
- Explains “who eats whom”
🟢 Food Web:
- Interconnected network of many food chains
- Shows complex feeding relationships
🟢 Trophic Level:
- Position of an organism in a food chain
- 1st: Producers → higher levels: consumers
🟢 Pollination:
- Transfer of pollen from stamens to carpels
- Essential for fruit and seed formation
🟢 Decomposition:
- Breakdown of dead organic matter
- Converts it into simpler substances
- Returns nutrients to the soil 🌱
🌈 Nature stays balanced when all parts work together — protecting nature means protecting our future! 🌍💚

