🧭 Chapter Overview
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be divided into different types based on how capable the AI system is and how it functions.
Understanding these types helps us know what AI can do today and what it might achieve in the future.
This chapter explains:
- The two major ways of classifying AI
- Examples of each type
- How AI evolves from simple to super-intelligent systems
4.1 Introduction to AI Types
💡 Definition:
AI systems are grouped into types based on:
- Capabilities – How much the AI can learn and evolve.
- Functionality – How the AI works or performs tasks.
🧩 Why Classification Is Important:
| Reason | Description |
|---|---|
| Understanding Growth | Shows how AI develops from simple to complex. |
| Technology Levels | Helps researchers build advanced systems. |
| Safety & Control | Helps identify what level of human supervision is needed. |
🧠 Mind Map: Introduction to AI Types
TYPES OF AI
|
---------------------------
| |
Based on Capabilities Based on Functionality
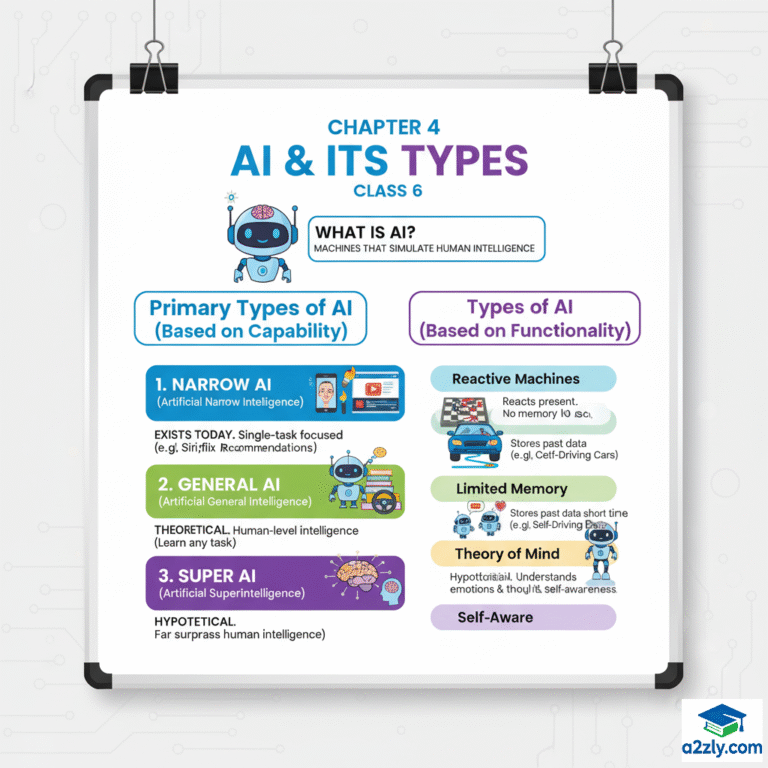
4.2 Types of Artificial Intelligence
There are two main categories to classify AI:
| Category | Basis | Number of Types | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Based on Capabilities | 3 Types | Narrow AI, General AI, Super AI |
| Type 2 | Based on Functionality | 4 Types | Reactive Machines, Limited Memory, Theory of Mind, Self-Aware AI |
🧠 Mind Map: Types of AI
Artificial Intelligence
|
--------------------------------
| |
Based on Capabilities Based on Functionality
| |
ANI, AGI, ASI Reactive, Limited Memory,
Theory of Mind, Self-Aware
4.3 AI Type–1: Based on Capabilities
This classification shows how capable or powerful an AI system is in terms of thinking, reasoning, and learning.
There are three main types 👇
1️⃣ Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
(Also known as Weak AI)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | AI designed to perform a single specific task. |
| Ability | Works within a limited pre-defined range. |
| Learning | Cannot learn beyond what it’s programmed for. |
| Example | Alexa, Siri, ChatGPT, Google Assistant, Chess AI. |
🧩 Key Idea:
Narrow AI ≈ One skill, one goal.
2️⃣ Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
(Also known as Strong AI)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | AI that can understand, learn, and apply knowledge like a human being. |
| Ability | Can perform multiple tasks and think independently. |
| Status | Still under research and development. |
| Example | Hypothetical — future human-like robots or Jarvis (Iron Man). |
🧩 Key Idea:
AGI ≈ AI that thinks like a human.
3️⃣ Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | AI that surpasses human intelligence and capabilities. |
| Ability | Can think, reason, and create beyond human imagination. |
| Risk | Might become uncontrollable if not ethically developed. |
| Example | Currently non-existent — only theoretical (like Ultron). |
🧩 Key Idea:
ASI ≈ AI smarter than all humans combined.
📊 Comparison Table – AI Based on Capabilities
| Type | Full Name | Also Known As | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | Artificial Narrow Intelligence | Weak AI | Focused on one task | Siri, Alexa, ChatGPT |
| 2️⃣ | Artificial General Intelligence | Strong AI | Thinks and reasons like humans | Research stage |
| 3️⃣ | Artificial Super Intelligence | Super AI | Beyond human intelligence | Theoretical (future AI) |
🧠 Mind Map: AI Based on Capabilities
AI Based on Capabilities
|
-----------------------------------------
| | |
Narrow (ANI) General (AGI) Super (ASI)
| | |
One Task Human-Level Beyond Human
Intelligence Intelligence Intelligence
4.4 AI Type–2: Based on Functionality
This classification shows how AI behaves and functions — how it uses memory, learning, and awareness to make decisions.
There are four major types 👇
1️⃣ Reactive Machines
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Basic AI that reacts to current situations without memory. |
| Ability | No learning from past data. |
| Decision Making | Only responds based on programmed logic. |
| Example | IBM’s Deep Blue (chess-playing computer). |
🧩 Key Idea:
Reactive AI = “If this happens, do that.”
2️⃣ Limited Memory AI
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | AI that learns from recent experiences to make better decisions. |
| Ability | Can store small amounts of data temporarily. |
| Use | Most modern AI systems use this model. |
| Example | Self-driving cars, voice assistants. |
🧩 Key Idea:
Limited Memory AI = “Learn from short-term experience.”
3️⃣ Theory of Mind AI
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | AI that can understand human emotions, intentions, and behavior. |
| Ability | Tries to predict human reactions and feelings. |
| Status | Under research and not yet achieved. |
| Example | AI with emotional understanding (like robots in movies). |
🧩 Key Idea:
Theory of Mind AI = “AI that understands people.”
4️⃣ Self-Aware AI
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | AI that has its own consciousness and self-awareness. |
| Ability | Can think, plan, and feel emotions like humans. |
| Status | Purely theoretical (future concept). |
| Example | Fictional AI — Ultron, Ava (Ex Machina). |
🧩 Key Idea:
Self-Aware AI = “AI that knows it exists.”
📊 Comparison Table – AI Based on Functionality
| Type | Name | Key Feature | Memory | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | Reactive Machines | Reacts only to current input | ❌ No memory | IBM Deep Blue |
| 2️⃣ | Limited Memory | Learns from past data | ✅ Short-term | Self-driving car |
| 3️⃣ | Theory of Mind | Understands human emotions | 🔄 In research | Emotional robots |
| 4️⃣ | Self-Aware | Self-conscious, independent | ♾️ Infinite (theoretical) | Ultron (fictional) |
🧠 Mind Map: AI Based on Functionality
AI Based on Functionality
|
---------------------------------------------
| | | |
Reactive Limited Theory of Mind Self-Aware
Machines Memory AI AI
| | | |
No Memory Short-term Emotional Conscious
Response Learning AI (Future) AI (Future)
📘 Summary Table: Chapter 4 – AI and Its Types
| Section | Topic | Key Idea |
|---|---|---|
| 4.1 | Introduction | AI classified by Capabilities and Functionality |
| 4.2 | Types of AI | Two categories → Capability-based & Functionality-based |
| 4.3 | Based on Capabilities | ANI, AGI, ASI — from weak to super-intelligent |
| 4.4 | Based on Functionality | Reactive, Limited Memory, Theory of Mind, Self-Aware |
✅ Key Takeaways
- AI is divided into two major categories:
- Based on Capabilities:
1️⃣ Narrow AI (ANI)
2️⃣ General AI (AGI)
3️⃣ Super AI (ASI) - Based on Functionality:
1️⃣ Reactive Machines
2️⃣ Limited Memory
3️⃣ Theory of Mind
4️⃣ Self-Aware AI
- Based on Capabilities:
- Most AI today is Narrow and Limited Memory AI (e.g., Alexa, Siri, ChatGPT).
- Super AI and Self-Aware AI are still concepts of the future.
🧠 Complete Mind Map: AI and Its Types
AI AND ITS TYPES
|
--------------------------------------------------
| |
Based on Capabilities Based on Functionality
| |
------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
| | | | | | |
Narrow AI General AI Super AI Reactive Limited Theory of Self-
(ANI) (AGI) (ASI) Machines Memory AI Mind AI Aware AI
| | | | | | |
Single-Task Human-Like Beyond Human No Memory Short-Term Understand Conscious
AI Intelligence Intelligence Logic Learning Emotions Existence