🌟 Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is shaping the way we live, learn, and interact with technology. From predicting weather patterns to powering smart assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant, AI is everywhere around us.
To truly understand AI, we must explore its Domains — specialized areas where machines “think” and perform intelligent tasks.
💡 Focus Keyword: The Domains of Artificial Intelligence Class 7 include Data Science, Computer Vision, and Natural Language Processing (NLP) — each helping machines learn, see, and understand in unique ways.
In this guide, we’ll explore these domains, their applications, and how AI contributes to sustainability, global goals (SDGs), and systems thinking — all while developing 21st-century skills among students.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
📘 1.1 Introduction to Domain
A domain in Artificial Intelligence refers to a specific area of knowledge or expertise where AI systems operate.
Just as humans specialize in different professions — a doctor treats patients, a teacher educates students — AI systems specialize in solving problems within their domain of expertise.
🧠 Example:
- An AI that detects faces in photos belongs to the Computer Vision domain.
- A chatbot that answers questions belongs to Natural Language Processing (NLP).
- A system predicting tomorrow’s weather belongs to Data Science.
🌍 Why Domains Matter in AI
- Define the type of data AI uses.
- Determine the skills and algorithms AI needs.
- Decide how AI interacts with humans and the world.
Thus, the Domains of Artificial Intelligence Class 7 form the foundation for all smart systems — helping machines process images, numbers, and language just like humans.
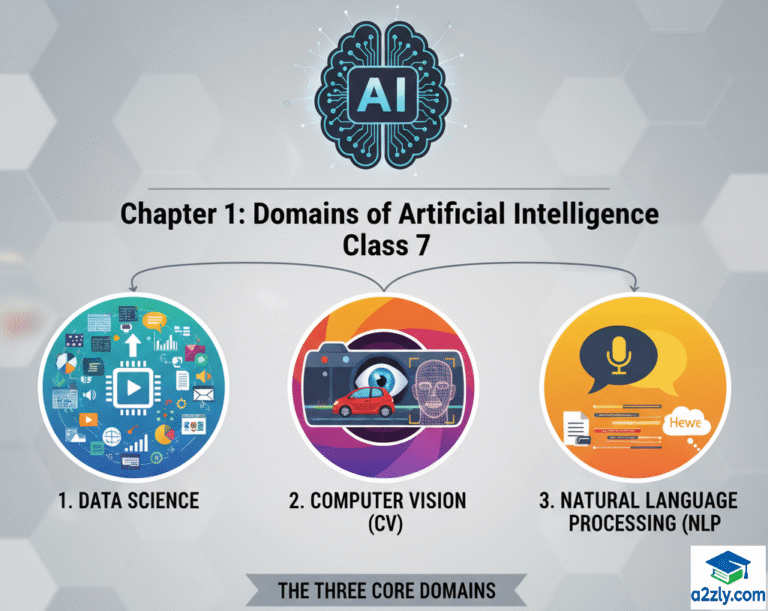
🧩 1.2 Types of Domains in Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is divided into three major domains, each focusing on a specific kind of data and task.
🟦 1. Data Science
- Deals with numerical data, statistics, and patterns.
- Helps AI systems analyze information and make predictions.
- Example: Predicting exam results or weather patterns.
🟩 2. Computer Vision (CV)
- Helps machines see and interpret images or videos.
- Example: Face recognition systems in mobile phones or CCTV cameras.
🟨 3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Allows AI to understand, interpret, and respond to human language.
- Example: Chatbots, translation tools, and voice assistants.
📘 Figure 1.1 – Domains of Artificial Intelligence Class 7
+-----------------------+
| Artificial |
| Intelligence |
+-----------+------------+
|
-------------------------------------------------
| | |
+----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------------+
| Data Science | | Computer | | Natural Language |
| (Numbers, | | Vision (CV) | | Processing (NLP) |
| Patterns) | | (Images, | | (Text, Speech) |
| | | Videos) | | |
+----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------------+
Alt Text: Domains of Artificial Intelligence Class 7 – Data Science, Computer Vision, and NLP diagram.
💡 1.3 Introduction to AI Domains Using Applications
Each domain connects AI with real-world examples.
Let’s explore how these three domains make our daily lives smarter.
📊 1.3.1 Applications of Data Science
Data Science is the analytical brain of AI. It helps systems learn from numbers and patterns to make decisions.
| Field | AI Application | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Disease prediction | AI studies patient data to diagnose illnesses early. |
| Weather | Forecasting | Predicts rainfall or storms using climate data. |
| Finance | Stock prediction | AI analyzes stock trends and market risks. |
| Education | Smart grading | Tracks student performance data. |
| Transportation | Route optimization | Suggests best travel routes using traffic data. |
💬 Real-Life Example:
Google Maps uses Data Science and AI to suggest the fastest route based on real-time traffic patterns.
💬 1.3.2 Applications of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP helps machines understand human languages — spoken or written.
| Application | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Chatbots | Text conversation | Customer support on websites. |
| Voice Assistants | Speech-to-action | Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. |
| Language Translation | Converts one language to another | Google Translate. |
| Grammar Correction | Improves writing | Grammarly and AI writing tools. |
| Text Summarization | Shortens content | AI tools summarizing long articles. |
💡 Example:
When you say “Play music”, Alexa uses NLP to understand your words and trigger a music-playing action.
👁️ 1.3.3 Applications of Computer Vision (CV)
Computer Vision gives AI the ability to “see” and interpret visual data.
| Application | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Face Recognition | Identifies people | Used in security and phones. |
| Self-Driving Cars | Detects objects on roads | AI recognizes signals and pedestrians. |
| Medical Imaging | Analyzes scans | Detects diseases from X-rays and MRIs. |
| Agriculture | Monitors crops | AI detects pests or crop health using images. |
| Robotics | Visual navigation | Robots identify and pick objects. |
💬 Example:
AI-powered cameras use Computer Vision to blur backgrounds automatically — a perfect selfie tool!
🌱 1.4 Artificial Intelligence: Exploring Sustainability
Artificial Intelligence is not only about machines — it’s about building a smarter and sustainable future.
AI is used to:
- Save energy.
- Reduce waste.
- Improve agriculture and healthcare.
- Protect the environment.
🧠 Classroom Connection:
When students design AI projects (like Smart Irrigation), they contribute to sustainable innovation.
🌍 1.4.1 Sustainability
Sustainability means using resources in a way that meets today’s needs without harming the planet for future generations.
AI supports sustainability by:
- Monitoring pollution and deforestation.
- Designing smart waste management systems.
- Helping farmers optimize crop yields.
- Promoting clean energy usage.
💡 Example:
AI drones are used to plant trees in deforested areas — a sustainable innovation!
♻️ 1.4.2 The 3Ps of Sustainability: People, Planet, and Profit
| P | Description | AI Example |
|---|---|---|
| 👥 People | Social equality and better living | AI in healthcare and education. |
| 🌍 Planet | Environmental protection | AI in climate prediction. |
| 💰 Profit | Economic growth with ethics | AI in green businesses and automation. |
Focus Keyword: Domains of Artificial Intelligence Class 7 connects sustainability with innovation — making students responsible creators.
💚 1.4.3 Why Sustainability Matters for Society
Without sustainability, we risk pollution, inequality, and resource shortage.
AI helps maintain the balance between human progress and environmental responsibility.
💡 Example: AI predicting floods helps save lives and property — a perfect mix of technology and empathy.
🌍 1.5 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The United Nations’ 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim to make the world better by 2030 — and AI helps achieve many of them.
| SDG | AI Contribution |
|---|---|
| Zero Hunger (SDG 2) | Predicts crop yield and prevents food waste. |
| Quality Education (SDG 4) | Personalized learning systems. |
| Clean Water (SDG 6) | Detects water contamination using sensors. |
| Clean Energy (SDG 7) | Smart energy grids and optimization. |
| Climate Action (SDG 13) | Predicts natural disasters and monitors pollution. |
💡 Real-Life Impact:
AI systems are used by the UNESCO to track ocean plastic and reduce pollution (source).
⚙️ 1.6 What Actually is Systems Thinking?
Systems Thinking is an approach that helps understand how different parts of a system are connected and influence one another.
In AI, Systems Thinking means:
- Seeing the bigger picture.
- Identifying how data, sensors, and algorithms work together.
- Understanding feedback and improving system efficiency.
💬 Example:
A Smart Traffic System doesn’t just focus on signals — it includes cars, pedestrians, sensors, and weather data to manage roads safely.
🧩 1.6.1 Why Systems Thinking Helps
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Holistic Understanding | Helps visualize all parts of a system. |
| Problem-Solving | Simplifies complex issues into manageable parts. |
| Innovation | Encourages creativity and efficient AI solutions. |
| Collaboration | Promotes teamwork and shared responsibility. |
💡 In CBSE AI projects, students use Systems Thinking to plan before coding.
🗺️ 1.7 System Maps
A System Map is a visual representation of how different parts of an AI system interact.
It includes:
- Inputs (data)
- Processes (AI algorithms)
- Outputs (results/actions)
- Feedback Loops (continuous improvement)
🖼️ Example System Map: Smart Irrigation AI
+-----------------+ +--------------------+ +---------------------+
| Moisture Sensor | -----> | AI Controller | -----> | Water Pump Control |
| (Input Data) | | (Processes Data) | | (Output Action) |
+-----------------+ +--------------------+ +---------------------+
^ |
| v
+---------------- Feedback from Soil Moisture --------------+
💡 Explanation:
The Moisture Sensor collects data → AI decides whether to water → Water Pump acts → sensor sends feedback — completing a sustainable loop.
🧭 1.7.1 Purpose of System Maps
| Purpose | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Visualize how AI systems work | Improves understanding |
| Identify data flow | Enhances planning |
| Encourage teamwork | Builds communication |
| Plan projects effectively | Supports innovation |
🧠 Summary of Chapter 1 – Domains of Artificial Intelligence Class 7
- A Domain is a specialized area of AI operation.
- AI has three key domains — Data Science, Computer Vision, and NLP.
- AI connects with sustainability and SDGs to make the world better.
- Systems Thinking teaches holistic analysis and planning.
- System Maps help visualize AI system structure.
📚 Exercise Section
🧩 1. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Choose the correct option:
- A specific area of knowledge or expertise in which an AI system works is called a —
A. Network
B. Domain
C. Database
D. Algorithm
Answer: B - Which AI domain deals with understanding human language?
A. Data Science
B. Robotics
C. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
D. Computer Vision
Answer: C - An AI that recognizes faces in photos belongs to which domain?
A. NLP
B. Computer Vision
C. Data Science
D. Cybersecurity
Answer: B - Predicting exam results or weather patterns is an example of —
A. NLP
B. Data Science
C. Computer Vision
D. Robotics
Answer: B - Which of these AI tools uses Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
A. Google Maps
B. Alexa
C. Face Unlock
D. Self-Driving Car
Answer: B - The AI domain that helps machines “see” and interpret images or videos is —
A. NLP
B. Data Science
C. Computer Vision
D. Machine Learning
Answer: C - In sustainability, the “3Ps” stand for —
A. Power, People, Planet
B. People, Planet, Profit
C. Process, Planet, Progress
D. People, Product, Policy
Answer: B - AI predicting floods or natural disasters helps achieve which SDG?
A. Zero Hunger
B. Clean Water
C. Climate Action
D. Quality Education
Answer: C - Systems Thinking helps in —
A. Understanding parts of a system separately
B. Understanding how parts of a system connect and interact
C. Ignoring feedback
D. Coding faster
Answer: B - The main purpose of a System Map is to —
A. Show the history of AI
B. Display data only
C. Visualize how AI systems work
D. Create pictures
Answer: C
✍️ Answer Key (MCQs)
1-B | 2-C | 3-B | 4-B | 5-B | 6-C | 7-B | 8-C | 9-B | 10-C
✨ 2. Fill in the Blanks
- A domain in AI refers to a specific area of __________.
Answer: knowledge or expertise - The three main domains of AI are Data Science, __________, and NLP.
Answer: Computer Vision - Data Science helps AI systems to learn from __________ and patterns.
Answer: numbers - NLP stands for __________.
Answer: Natural Language Processing - Computer Vision enables AI to understand __________ data.
Answer: visual - Sustainability focuses on balancing People, Planet, and __________.
Answer: Profit - AI-based drones are used for __________ trees in deforested areas.
Answer: planting - Systems Thinking helps in understanding how different parts of a system are __________.
Answer: connected - Smart Irrigation uses sensors and AI to manage __________ efficiently.
Answer: water - AI supports SDG 4 by improving access to __________ education.
Answer: quality
⚖️ 3. Assertion–Reason Questions
Directions: For each question, select the correct option:
(A) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation.
(B) Both are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation.
(C) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(D) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
- Assertion: Data Science helps AI systems make predictions.
Reason: It allows machines to understand spoken language.
Answer: C - Assertion: Computer Vision enables AI to recognize images.
Reason: It deals with text and voice-based data.
Answer: C - Assertion: NLP is used in chatbots and translators.
Reason: It helps AI understand and respond to human languages.
Answer: A - Assertion: Sustainability is about using resources wisely for the future.
Reason: AI contributes to sustainability by monitoring pollution and improving energy use.
Answer: A - Assertion: System Maps show how AI systems interact.
Reason: They only represent hardware components.
Answer: C
💬 4. Very Short Answer Type Questions (VSAQs)
(Answer in one to two lines)
- What is a domain in Artificial Intelligence?
Answer: A domain is a specific area where AI systems perform specialized tasks. - Name the three domains of AI.
Answer: Data Science, Computer Vision, and Natural Language Processing (NLP). - What does NLP enable AI to do?
Answer: Understand, interpret, and respond to human language. - Give one example of Computer Vision.
Answer: Face recognition in smartphones. - Define Data Science.
Answer: Data Science involves analyzing data to identify patterns and make predictions. - What is sustainability?
Answer: Using resources responsibly to meet present needs without harming the future. - List the 3Ps of sustainability.
Answer: People, Planet, and Profit. - What is Systems Thinking?
Answer: An approach that studies how different parts of a system interact. - Mention one AI application in agriculture.
Answer: AI monitors crop health using image data. - What is the purpose of a System Map?
Answer: To show how inputs, processes, and outputs connect within a system.
📘 5. Short Answer Type Questions (SAQs)
(Answer in 2–3 sentences)
- Explain why domains are important in AI.
Answer: Domains help AI systems focus on specific types of data and problems, enabling them to use the right tools and algorithms for each task. - Differentiate between NLP and Computer Vision.
Answer: NLP works with text and speech data to understand human language, while Computer Vision interprets images and videos. - How does Data Science help in decision-making?
Answer: It analyzes large sets of numerical data to find patterns and predict future outcomes. - Give two examples of how AI supports sustainability.
Answer: AI predicts natural disasters to save lives and optimizes energy use to reduce waste. - What role does AI play in achieving SDGs?
Answer: AI aids in goals like Zero Hunger, Quality Education, and Climate Action by providing smart, data-driven solutions. - Describe the 3Ps of sustainability with one example.
Answer: People (healthcare), Planet (pollution control), and Profit (green business) are balanced by AI for sustainable growth. - How does Systems Thinking improve AI projects?
Answer: It helps students plan and understand how data, algorithms, and sensors work together in an AI system. - What is an example of an AI-based sustainable innovation?
Answer: AI-powered drones planting trees to restore forests. - Why is feedback important in System Maps?
Answer: Feedback helps AI systems learn and improve continuously based on outcomes. - Give one classroom example of Systems Thinking.
Answer: Students creating a Smart Irrigation model using sensors, AI, and feedback loops.
🧠 6. Long Answer Type Questions (LAQs)
(Answer in 5–8 sentences)
- Explain the three main domains of Artificial Intelligence with examples.
Answer: The three main domains are Data Science, Computer Vision, and Natural Language Processing. Data Science analyzes data for predictions like weather forecasts. Computer Vision allows AI to recognize images, such as face detection in cameras. NLP helps AI understand human language, like in Alexa or chatbots. Together, they form the foundation for modern intelligent systems. - Discuss how AI contributes to sustainability and SDGs.
Answer: AI supports sustainability by conserving resources, reducing waste, and promoting clean energy. It helps achieve SDGs like Zero Hunger (through crop prediction) and Climate Action (through disaster forecasting). By integrating AI with responsible innovation, we move toward a greener and fairer world. - What is Systems Thinking? Explain its importance in AI projects.
Answer: Systems Thinking studies how parts of a system connect and influence one another. In AI, it helps identify how data inputs, algorithms, and feedback loops work together. This approach promotes problem-solving, teamwork, and innovation — essential for real-world AI applications. - Describe the structure and use of a System Map in AI.
Answer: A System Map visually represents how an AI system functions — showing inputs, processes, outputs, and feedback. For example, in Smart Irrigation, sensors (inputs) send data to the AI (process), which controls water pumps (output). Feedback from soil moisture ensures continuous improvement. - How does AI build 21st-century skills among students?
Answer: AI education enhances creativity, critical thinking, collaboration, and systems thinking. Students learn to solve real-life problems responsibly, connecting technology with sustainability and innovation.
📘 7. Source-Based / Case-Based Assessment Question
📘 Source-Based Question 1
Source Extract:
“Artificial Intelligence is helping farmers achieve sustainable growth. AI systems analyze soil data to decide when and how much to irrigate. Sensors collect real-time information, and the AI controller activates pumps automatically. This not only saves water but also increases productivity.”
Questions:
- Which AI domain is primarily used in this case?
- How does the AI system receive input?
- Mention one sustainability benefit of this system.
- Explain how feedback helps in improving this AI model.
Answer Key:
- Data Science (combined with Computer Vision for sensor analysis).
- Through soil moisture sensors collecting input data.
- It saves water and supports sustainable farming.
- Feedback from soil sensors helps the system adjust irrigation automatically.
📘 Source-Based Question 2
Source Extract:
“Voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant have become part of our daily lives. When we say ‘Set an alarm for 6 AM’ or ‘Play my favorite song’, these AI systems understand our words and perform the action. They learn from user behavior and improve over time to give more accurate results.”
Questions:
- Which AI domain helps voice assistants understand human speech?
- Give one example of how these assistants make life easier.
- How does the system learn and improve with time?
- Identify one ethical or privacy issue that may arise with such systems.
Answer Key:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP).
- They perform voice-based commands like setting alarms or playing songs.
- By learning from user interactions and feedback (machine learning).
- Storing voice data may raise privacy concerns.
📗 Source-Based Question 3
Source Extract:
“A city uses AI-based CCTV cameras that can detect traffic violations like overspeeding and signal jumping. The system captures the vehicle number plate and automatically sends a challan (fine) to the owner. This reduces human error and ensures road safety.”
Questions:
- Which AI domain is applied in this system?
- Mention one advantage of using AI for traffic monitoring.
- How does this system promote sustainability or safety?
- Identify one limitation or challenge of such AI systems.
Answer Key:
- Computer Vision.
- It automatically detects rule violations, saving time and reducing manual work.
- Promotes safety by reducing accidents and ensuring disciplined driving.
- It may make mistakes in poor lighting or weather conditions, affecting accuracy.
📙 Source-Based Question 4
Source Extract:
“AI-based agricultural drones are now being used to spray fertilizers and monitor crop health. These drones analyze images of fields to detect pests or nutrient deficiencies. Farmers receive real-time data, helping them take timely action and reduce chemical use.”
Questions:
- Which two AI domains work together in this example?
- How do these drones contribute to sustainable farming?
- What kind of data does the AI system analyze?
- Explain one environmental benefit of this innovation.
Answer Key:
- Data Science and Computer Vision.
- They reduce chemical usage and improve crop yield by targeted spraying.
- Image data showing crop health and pest presence.
- Reduces pollution and soil damage caused by overuse of pesticides.
❓ FAQ – Domains of Artificial Intelligence Class 7
Q1. What are the main domains of AI?
👉 Data Science, Computer Vision, and Natural Language Processing (NLP).
Q2. Why are domains important?
👉 They define the area in which AI operates — helping machines specialize in tasks like seeing, learning, or speaking.
Q3. How does AI help sustainability?
👉 By optimizing energy, predicting weather, and reducing waste.
Q4. What is Systems Thinking in AI?
👉 A way of understanding how different parts of an AI system work together.
Q5. What are System Maps?
👉 Diagrams that show data flow and interaction between AI components.
🔗 Internal Links (For Website Version)
- Chapter 2: Data Science in AI – Class 7 Guide
- AI Projects for Students (CBSE 2025–26)
- Digital Citizenship and AI Ethics
🌍 External References (Authoritative DoFollow Sources)
🏁 Conclusion
The Domains of Artificial Intelligence Class 7 serve as the building blocks of modern technology.
From Data Science that powers analytics to Computer Vision that helps AI see and NLP that makes it communicate — every domain adds intelligence and humanity to machines.
By integrating Sustainability, Systems Thinking, and SDGs, students not only learn technology — they learn responsibility, empathy, and innovation.
The future of AI isn’t just about smarter machines — it’s about smarter, kinder, and more sustainable humans. 🌍✨