🧭 Chapter Overview
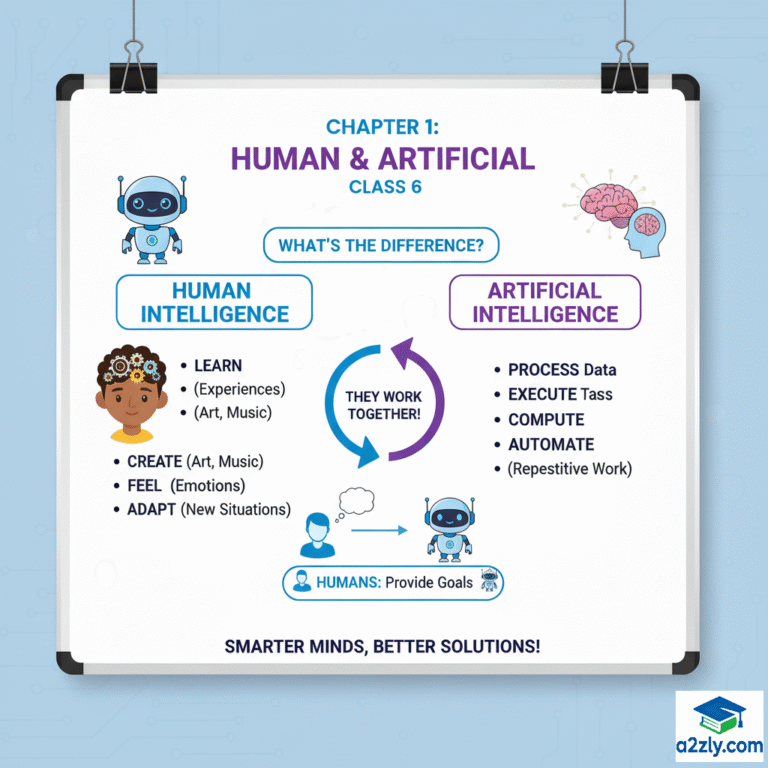
Humans are intelligent beings — we think, learn, and solve problems.machines can also learn, think, and make decisions — this is called Artificial Intelligence (AI) .
This chapter helps us understand:
What intelligence means
The difference between human and artificial intelligence
Why we need AI and how it works
1.1 Introduction to Intelligence 💡 Definition:
Intelligence is the ability to think, learn, understand, and solve problems .
🧠 In Simple Words:
Intelligence means using knowledge and experience to act wisely .
📋 Example:
Situation Intelligent Action You see rain clouds You carry an umbrella 🌂 You forget a fact You look it up or recall it from memory You face a puzzle You find patterns and solve it
🧠 Mind Map: Introduction to Intelligence
Intelligence
|
-----------------------------
| | |
Thinking Learning Solving
1.2 What is Intelligence Made Of? Intelligence is not one single ability — it’s made of many components that help us think and act smartly.
⚙️ Main Components of Intelligence:
Component Description Example Learning Gaining knowledge or skills Learning a new language Reasoning Making logical decisions Choosing the best route Problem Solving Finding solutions to challenges Solving a riddle Perception Understanding surroundings using senses Seeing, hearing, or touching Memory Storing and recalling information Remembering your friend’s birthday Creativity Creating new ideas or art Painting or inventing a new tool
🧠 Mind Map: What Intelligence is Made Of
Components of Intelligence
|
-------------------------------------
| | | | |
Learning Reasoning Problem Memory Creativity
Solving
1.3 Types of Intelligence According to psychologist Howard Gardner , there are multiple types of intelligence — every person has different combinations of them.
🧩 Main Types of Human Intelligence:
Type Description Example Linguistic Intelligence Skill in using words and language Writers, poets Logical–Mathematical Intelligence Reasoning and problem-solving Scientists, engineers Spatial Intelligence Visualizing and designing space Artists, architects Bodily–Kinesthetic Intelligence Control of body movements Dancers, athletes Musical Intelligence Understanding rhythm and sound Singers, musicians Interpersonal Intelligence Understanding others’ emotions Teachers, leaders Intrapersonal Intelligence Self-awareness and reflection Philosophers Naturalistic Intelligence Understanding nature and animals Biologists, farmers
🧠 Mind Map: Types of Intelligence
Types of Intelligence
|
--------------------------------------------------
| | | | | |
Logical Linguistic Musical Spatial Interpersonal Naturalistic
1.4 Difference Between Human Intelligence and Machine Intelligence Feature Human Intelligence Machine Intelligence Nature Natural (biological brain) Artificial (programmed) Learning From experience and emotion From data and patterns Creativity High (can imagine new things) Limited (follows code) Decision Making Based on logic + emotion Based on logic only Adaptability Can adjust to new situations Needs reprogramming Speed Slower in calculations Extremely fast Error Rate Can make mistakes Fewer mistakes if coded right
🧠 Mind Map: Human vs Machine Intelligence
Human vs Machine Intelligence
|
--------------------------------------
| | |
Human Machine Comparison
(Emotional) (Logical) (Speed, Accuracy)
1.5 Artificial Intelligence 💡 Definition:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the branch of computer science that enables machines to think, learn, and make decisions like humans.
⚙️ In Simple Words:
AI means teaching computers to act smartly — like recognizing speech, playing games, or driving cars.
🧩 Examples of AI:
AI Application What It Does Google Assistant Understands speech & answers ChatGPT Generates text like a human Self-driving Cars Detects and reacts to objects Face Recognition Identifies people from photos
🧠 Mind Map: Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
|
----------------------------------------
| | | |
Learning Reasoning Problem Decision
Ability Solving Making
1.6 Why We Need Artificial Intelligence AI helps solve problems that are too complex, repetitive, or data-heavy for humans.
⚙️ Reasons We Need AI:
Reason Description Automation Reduces human effort in repetitive work Speed & Accuracy Performs tasks faster and more precisely Data Handling Manages and analyzes big data Consistency Never gets tired or emotional Innovation Helps invent new technologies
1.6.1 Goals of Artificial Intelligence Goal Description Understanding Human Intelligence To learn how humans think and solve problems Automation of Tasks Make machines perform routine or dangerous tasks Problem Solving Create systems that find solutions automatically Human–AI Collaboration Help humans make better decisions Adaptability Make AI systems learn and improve over time
🧠 Mind Map: Why We Need AI
Why We Need AI
|
------------------------------
| | | |
Speed Accuracy Automation Innovation
1.7 Subjects Included in Artificial Intelligence AI is an interdisciplinary field , meaning it includes knowledge from many other subjects.
Subject Role in AI Mathematics Used for algorithms and logical reasoning Computer Science Builds the software and models Psychology Helps understand human thinking Neuroscience Studies how the brain works Statistics Helps in data analysis and predictions Linguistics Helps AI understand human language Philosophy Deals with ethical aspects of AI
🧠 Mind Map: Subjects in AI
Subjects in AI
|
---------------------------------
| | | | |
Math CS Psychology Statistics Linguistics
1.8 Advantages of Artificial Intelligence Advantage Description Example Efficiency Works faster and longer than humans 24/7 customer chatbots Accuracy Fewer errors than humans Medical diagnosis systems Automation Replaces manual work Manufacturing robots Decision Making Data-driven decisions Stock market AI tools Risk Handling Works in dangerous areas Space exploration robots
🧠 Mind Map: Advantages of AI
Advantages of AI
|
-----------------------------
| | | |
Speed Accuracy Safety Automation
1.9 Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence Disadvantage Description Example Job Loss Automation may replace human workers Robots in factories Costly AI systems are expensive to build and maintain AI labs and supercomputers No Emotions Cannot understand human feelings Lacks empathy Data Privacy Misuse of user data Social media tracking Bias & Error AI may learn wrong patterns Unfair hiring or facial recognition bias
🧠 Mind Map: Disadvantages of AI
Disadvantages of AI
|
-----------------------------
| | | |
Job Loss Cost Bias No Emotion
1.10 Introduction to AI Domains (Data, CV & NLP) AI is divided into several domains , each focusing on a specific ability of machines.
AI Domain Full Form Description Example Data Science — Deals with analyzing and predicting from data Weather forecasting, fraud detection Computer Vision (CV) — Enables machines to see and interpret images Face detection, object tracking Natural Language Processing (NLP) — Allows computers to understand and generate human language Chatbots, translation tools
🧩 Examples Explained:
Data Science: AI analyzes large data sets to find useful patterns (like predicting diseases).Computer Vision: Cameras + AI = can “see” objects and recognize faces.NLP: AI understands text and voice commands (“Hey Google!”).
🧠 Mind Map: AI Domains
AI Domains
|
-----------------------------
| | |
Data Computer Natural
Science Vision Language
Processing
📘 Summary Table: Chapter 1 – Human and Artificial Intelligence
Section Topic Key Idea 1.1 Introduction Intelligence is the ability to think, learn, and act wisely 1.2 Components Intelligence includes learning, memory, reasoning, etc. 1.3 Types Human intelligence has multiple forms like linguistic, logical, etc. 1.4 Human vs Machine Humans are emotional; machines are logical 1.5 AI Definition AI enables machines to think and learn like humans 1.6 Need & Goals AI increases speed, efficiency, and supports innovation 1.7 Subjects AI combines maths, CS, psychology, and statistics 1.8 Advantages Fast, accurate, tireless, and risk-handling 1.9 Disadvantages Costly, job loss, data bias, lacks emotion 1.10 AI Domains Data Science, Computer Vision, and NLP are core AI fields
✅ Key Takeaways
Intelligence = ability to think, learn, and act wisely.Human Intelligence comes naturally; AI is created by humans.AI is used in education, healthcare, industry, and daily life .
AI’s main goals: learning, reasoning, and problem-solving.
Ethical and responsible AI use ensures fairness and safety.
🧠 Complete Mind Map: Human & Artificial Intelligence
HUMAN & ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| | | | | | | |
Intelligence Types Human vs Machine AI Definition Need Subjects Pros Cons Domains
| | | |
Learning, Reasoning, etc. Goals: Automation, Speed Data CV NLP